The inhibitory effect and mechanism of quetiapine on tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo
- PMID: 34626444
- PMCID: PMC9293313
- DOI: 10.1002/tox.23380
The inhibitory effect and mechanism of quetiapine on tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo
Abstract
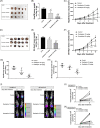
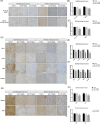
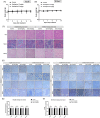
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the primary tumor of the liver and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death. Recently, several studies indicated the anti-tumor potential of antipsychotic medicine. Quetiapine, an atypical antipsychotic, is used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder since 1997. However, whether quetiapine may show potential to suppress HCC progression and its underlying mechanism is persisting unclear. Quetiapine has been shown to induce apoptosis and inhibit invasion ability in HCC in vitro. Here, we established two different HCC (Hep3B, SK-Hep1) bearing animals to identify the treatment efficacy of quetiapine. Tumor growth, signaling transduction, and normal tissue pathology after quetiapine treatment were validated by caliper, bioluminescence image, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and hematoxylin and eosin staining, respectively. Quetiapine suppressed HCC progression in a dose-dependent manner. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) and Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) mediated downstream proteins, such as myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (MCL-1), cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (C-FLIP), X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), Cyclin-D1, matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9), vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) which involved in proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, invasion and anti-tumor immunity were all decreased by quetiapine. In addition, extrinsic/intrinsic caspase-dependent and caspase-independent pathways, including cleaved caspase-3, -8, and - 9 were increased by quetiapine. In sum, the tumor inhibition that results from quetiapine may associate with ERK and NF-κB inactivation.
Keywords: ERK; NF-κB; hepatocellular carcinoma; quetiapine.
© 2021 The Authors. Environmental Toxicology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ERK/AKT Inactivation and Apoptosis Induction Associate With Quetiapine-inhibited Cell Survival and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.In Vivo. 2020 Sep-Oct;34(5):2407-2417. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12054. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32871766 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis induction and ERK/NF-κB inactivation are associated with magnolol-inhibited tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo.Environ Toxicol. 2020 Feb;35(2):167-175. doi: 10.1002/tox.22853. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Environ Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31714653
-
Fluoxetine Induces Apoptosis through Extrinsic/Intrinsic Pathways and Inhibits ERK/NF-κB-Modulated Anti-Apoptotic and Invasive Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 11;20(3):757. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030757. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30754643 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib inhibits tumor progression through suppression of ERK/NF-κB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma bearing mice.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 8;38(3):BSR20171264. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171264. Print 2018 Jun 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29535278 Free PMC article.
-
Glycyrrhizic Acid Modulates Apoptosis through Extrinsic/Intrinsic Pathways and Inhibits Protein Kinase B- and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Mediated Metastatic Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma In Vitro and In Vivo.Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(1):223-244. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500123. Am J Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 32054305
Cited by
-
Synthesis Folate-linked Chitosan-coated Quetiapine/BSA Nano-Carriers as the Efficient Targeted Anti-Cancer Drug Delivery System.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep;66(9):2297-2307. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00858-0. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37633875
-
First-Line Combination Treatment with Low-Dose Bipolar Drugs for ABCB1-Overexpressing Drug-Resistant Cancer Populations.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 7;24(9):8389. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098389. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The OSR9 Regimen: A New Augmentation Strategy for Osteosarcoma Treatment Using Nine Older Drugs from General Medicine to Inhibit Growth Drive.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15474. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015474. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated plasma matrix metalloproteinase 9 in schizophrenia patients associated with poor antipsychotic treatment response and white matter density deficits.Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2024 Aug 27;10(1):71. doi: 10.1038/s41537-024-00494-w. Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39191778 Free PMC article.
-
Quetiapine Significantly Improves the Effectiveness of Radiotherapy in Combating Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression in a Hep3B Xenograft Mouse Model.In Vivo. 2024 May-Jun;38(3):1079-1093. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13542. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38688627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meltzer HY. Update on typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Annu Rev Med. 2013;64:393‐406. doi:10.1146/annurev‐med‐050911‐161504 - PubMed
-
- Chen VC, Chan HL, Hsu TC, et al. New use for old drugs: the protective effect of atypical antipsychotics on hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2019;144(10):2428‐2439. doi:10.1002/ijc.31980 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

