Bi-allelic variants in SPATA5L1 lead to intellectual disability, spastic-dystonic cerebral palsy, epilepsy, and hearing loss
- PMID: 34626583
- PMCID: PMC8546233
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.08.003
Bi-allelic variants in SPATA5L1 lead to intellectual disability, spastic-dystonic cerebral palsy, epilepsy, and hearing loss
Abstract
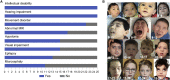
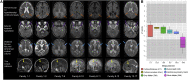
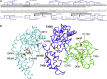
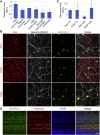
Spermatogenesis-associated 5 like 1 (SPATA5L1) represents an orphan gene encoding a protein of unknown function. We report 28 bi-allelic variants in SPATA5L1 associated with sensorineural hearing loss in 47 individuals from 28 (26 unrelated) families. In addition, 25/47 affected individuals (53%) presented with microcephaly, developmental delay/intellectual disability, cerebral palsy, and/or epilepsy. Modeling indicated damaging effect of variants on the protein, largely via destabilizing effects on protein domains. Brain imaging revealed diminished cerebral volume, thin corpus callosum, and periventricular leukomalacia, and quantitative volumetry demonstrated significantly diminished white matter volumes in several individuals. Immunofluorescent imaging in rat hippocampal neurons revealed localization of Spata5l1 in neuronal and glial cell nuclei and more prominent expression in neurons. In the rodent inner ear, Spata5l1 is expressed in the neurosensory hair cells and inner ear supporting cells. Transcriptomic analysis performed with fibroblasts from affected individuals was able to distinguish affected from controls by principal components. Analysis of differentially expressed genes and networks suggested a role for SPATA5L1 in cell surface adhesion receptor function, intracellular focal adhesions, and DNA replication and mitosis. Collectively, our results indicate that bi-allelic SPATA5L1 variants lead to a human disease characterized by sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) with or without a nonprogressive mixed neurodevelopmental phenotype.
Keywords: AAA+ superfamily; ATPase; SPATA5L1; cerebral palsy; epilepsy; intellectual disability; movement disorder; neurodevelopmental disorder; sensorineural hearing loss.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Liu Y., Black J., Kisiel N., Kulesz-Martin M.F. SPAF, a new AAA-protein specific to early spermatogenesis and malignant conversion. Oncogene. 2000;19:1579–1588. - PubMed
-
- Kubo Y., Imaizumi T., Ando M., Nakatochi M., Yasuda Y., Honda H., Kuwatsuka Y., Kato S., Kikuchi K., Kondo T. Association between kidney function and genetic polymorphisms in atherosclerotic and chronic kidney diseases: A cross-sectional study in Japanese male workers. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0185476. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G1000848/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT093205 MA /WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MR/N025431/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R00 HL143036/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL143036/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N025431/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N010035/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/V009346/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS106298/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/S006753/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS107428/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- WT104033AIA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

