A guide to senolytic intervention in neurodegenerative disease
- PMID: 34627838
- PMCID: PMC8627445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2021.111585
A guide to senolytic intervention in neurodegenerative disease
Abstract
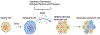
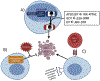
Cellular senescence is a potential tumor-suppressive mechanism that generally results in an irreversible cell cycle arrest. Senescent cells accumulate with age and actively secrete soluble factors, collectively termed the 'senescence-associated secretory phenotype' (SASP), which has both beneficial and detrimental effects. Although the contribution of senescent cells to age-related pathologies has been well-established outside the brain, emerging evidence indicates that brain cells also undergo cellular senescence and contribute to neuronal loss in the context of age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Contribution of senescent cells in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders has led to the possibility of eliminating senescence cells via pharmacological compounds called senolytics. Recently several senolytics have been demonstrated to elicit improved cognitive performance and healthspan in mouse models of neurodegeneration. However, their translation for use in the clinic still holds several potential challenges. This review summarizes available senolytics, their purported mode of action, and possible off-target effects. We also discuss possible alternative strategies that may help minimize potential side-effects associated with the senolytics approach.
Keywords: Aging; Immune surveillance; Neurodegeneration; Neurodegenerative diseases; Senescence; Senescence-associated secretory phenotype; Senolytic.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
None
Figures

References
-
- Acosta JC, Banito A, Wuestefeld T, Georgilis A, Janich P, Morton JP, Athineos D, Kang TW, Lasitschka F, Andrulis M, Pascual G, Morris KJ, Khan S, Jin H, Dharmalingam G, Snijders AP, Carroll T, Capper D, Pritchard C, Inman GJ, Longerich T, Sansom OJ, Benitah SA, Zender L, Gil J, 2013. A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat. Cell Biol 15, 978–990. 10.1038/ncb2784 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agostini A, Mondragõn L, Bernardos A, Martínez-Máñez R, Dolores Marcos M, Sancenõn F, Soto J, Costero A, Manguan-García C, Perona R, Moreno-Torres M, Aparicio-Sanchis R, Murguía JR, 2012. Targeted cargo delivery in senescent cells using capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed 10.1002/anie.201204663 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Amor C, Feucht J, Leibold J, Ho Y-J, Zhu C, Alonso-Curbelo D, Mansilla-Soto J, Boyer JA, Li X, Giavridis T, Kulick A, Houlihan S, Peerschke E, Friedman SL, Ponomarev V, Piersigilli A, Sadelain M, Lowe SW, 2020. Senolytic CAR T cells reverse senescence-associated pathologies. Nat. 2020 5837814 583, 127–132. 10.1038/s41586-020-2403-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

