Heart failure in diabetes
- PMID: 34627874
- PMCID: PMC8941799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154910
Heart failure in diabetes
Abstract
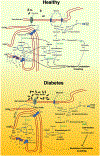
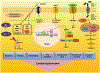
Heart failure and cardiovascular disorders represent the leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Here we present a systematic review of the main mechanisms underlying the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy. We also provide an excursus on the relative contribution of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts, endothelial and smooth muscle cells to the pathophysiology of heart failure in diabetes. After having described the preclinical tools currently available to dissect the mechanisms of this complex disease, we conclude with a section on the most recent updates of the literature on clinical management.
Keywords: Adrenergic receptors; Aging; BHB; Bioenergetics; Cardiomyocytes; Cardiovascular endocrinology; Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Diastolic dysfunction; Endothelium; FOXO1; Fibroblasts; Fibrosis; HFpEF; Heart failure; Mitochondria; NADH; Oxidative stress; ROS; Senescence; T1DM; T2DM; VSMC.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Nothing to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Balaban RS, Kantor HL, Katz LA, Briggs RW. Relation between work and phosphate metabolite in the in vivo paced mammalian heart. Science. 1986;232:1121–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

