Optimized amplification of BK polyomavirus in urine
- PMID: 34627948
- PMCID: PMC8881803
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114319
Optimized amplification of BK polyomavirus in urine
Abstract
BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) is a ubiquitous pathogen that typically results in asymptomatic infection. However, in immunocompromised individuals, BKPyV viral shedding in the urine can reach 109 copies per mL. These high viral levels within urine provide ideal samples for next-generation sequencing to accurately determine BKPyV genotype and identify mutations associated with pathogenesis. Sequencing data obtained can be further analyzed to better understand and characterize the genetic diversity present in BKPyV. Here, methods are described for the successful extraction of viral DNA from urine and the subsequent amplification methods to prepare a sample for next-generation sequencing.
Keywords: BK polyomavirus (BKPyV); Diversity; Genotype; Rolling circle amplification; Variation.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

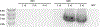
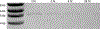

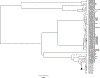
References
-
- Kluba J, Linnenweber-Held S, Heim A, Ang AM, Raggub L, Broecker V, Becker JU, Schulz TF, Schwarz A, Ganzenmueller T, 2015. A rolling circle amplification screen for polyomaviruses other than BKPyV in renal transplant recipients confirms high prevalence of urinary JCPyV shedding. Intervirology 58, 88–94. 10.1159/000369210. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

