Phosphate-triggered ratiometric fluoroimmunoassay based on nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion for sensitive detection of 1-naphthol for the exposure assessment of pesticide carbaryl
- PMID: 34629198
- PMCID: PMC8877597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127411
Phosphate-triggered ratiometric fluoroimmunoassay based on nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion for sensitive detection of 1-naphthol for the exposure assessment of pesticide carbaryl
Abstract
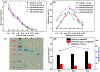
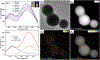
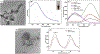
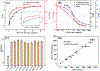
The excessive use of carbaryl has resulted in the risk of its exposure. In this study, we isolated six nanobodies (Nbs) from a camelid phage display library against the biomarker of carbaryl, 1-naphthol (1-NAP). Owing to its characteristics of easy genetic modifications, we produced a nanobody-alkaline phosphatase (Nb-CC4-ALP) fusion protein with good stability. A dual-emission system based ratiometric fluoroimmunoassay (RFIA) for quick and highly sensitive determination of 1-NAP was developed. Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) was used as an internal reference and for aggregation-induced emission enhancement (AIEE) of gold nanoclusters (AuNCs), while AuNCs could be quenched by MnO2 via oxidation. In the presence of ALP, ascorbic acid phosphate (AAP) can be transformed into ascorbic acid (AA), the later can etch MnO2 to recover the fluorescence of the AuNCs. Based on optimal conditions, the proposed assay showed 220-fold sensitivity improvement in comparison with conventional monoclonal antibody-based ELISA. The recovery test of urine samples and the validation by standard HPLC-FLD demonstrated the proposed assay was an ideal tool for screening 1-NAP and provided technical support for the monitoring of carbaryl exposure.
Keywords: 1-Naphthol; Carbaryl; Nanobody; Pesticide exposure; Ratiometric fluoroimmunoassay.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

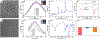

References
-
- Aprea C, Colosio C, Mammone T, Minoia C, Maroni M, 2002. Biological monitoring of pesticide exposure: a review of analytical methods. J. Chromatogr. B 769, 191–219. - PubMed
-
- Bartilotti M, Beluomini MA, Boldrin Zanoni MV, 2021. Using an electrochemical MIP sensor for selective determination of 1-naphthol in oilfield produced water. Electroanal. 33, 1346–1355.
-
- Berman T, Goeen T, Novack L, Beacher L, Grinshpan L, Segev D, Tordjman K, 2016. Urinary concentrations of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides in residents of a vegetarian community. Environ. Int 96, 34–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

