Sars-CoV2 vaccine hesitancy in Italy: A survey on subjects with diabetes
- PMID: 34629250
- PMCID: PMC8428984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.09.002
Sars-CoV2 vaccine hesitancy in Italy: A survey on subjects with diabetes
Abstract
Background and aims: Vaccine Hesitancy (VH) is a relevant obstacle for the COVID-19 vaccination campaign. The aim of this study is to assess the proportion of subjects unwilling to vaccinate among patients with type 1 (T1DM) and 2 (T2DM) diabetes, exploring factors associated with VH.
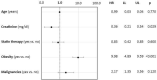
Methods and results: A purposely created interview was delivered from physicians to a consecutive series of adult (>18 years) subjects with diabetes referring to the Diabetes Outpatient Clinic of Careggi Hospital, Florence, from January 1st to April 30th 2021. Out of 502 subjects enrolled, 92 were vaccine hesitant respondents (18.3%); the corresponding figure for T1DM and T2DM was 13.0% (N = 14), and 19.9% (N = 78), respectively. After adjusting for age, higher HbA1c (1.07 [1.02-1.13], p = 0.008) and triglycerides levels (1.03 [1.01-1.06], p = 0.011) were positively associated with VH, among patients with T1DM. At multivariate analysis, after adjusting for age, creatinine, and statin use, patients with T2DM affected by obesity (9.98 [4.89-9.59], p < 0.01) and with lower levels of creatinine (0.36 [0.21-0.54], p = 0.029) were more likely to refuse COVID vaccination.
Conclusions: Hesitancy toward COVID-19 vaccination among subjects with diabetes is not negligible and seems to be more prevalent in individuals with lower adherence to medical prescriptions and/or reduced concerns over their health. This suggests the need for specific interventions to increase awareness and counter prejudices on vaccines.
Keywords: Covid-19; Diabetes; Obesity; Vaccine hesitancy.
Copyright © 2021 The Italian Diabetes Society, the Italian Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis, the Italian Society of Human Nutrition and the Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, Federico II University. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- della Salute Ministero. 2021. Piano vaccinale del commissario straordinario.https://www.governo.it/sites/governo.it/files/210313_Piano_Vaccinale_mar... [Internet]. [cited 2021 Mar 13]. Available from:
-
- Ramasamy M.N., Minassian A.M., Ewer K.J., Flaxman A.L., Folegatti P.M., Owens D.R., et al. Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): a single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet. 2020 Dec 19;396(10267):1979–1993. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johnson and Johnson: Sadoff J., Gray G., Vandebosch A., Cárdenas V., Shukarev G., Grinsztejn B., et al. ENSEMBLE Study Group Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021 Apr 21 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2101544. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33882225. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous