On Neurorights
- PMID: 34630057
- PMCID: PMC8498568
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.701258
On Neurorights
Abstract
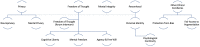
In recent years, philosophical-legal studies on neuroscience (mainly in the fields of neuroethics and neurolaw) have given increasing prominence to a normative analysis of the ethical-legal challenges in the mind and brain sciences in terms of rights, freedoms, entitlements and associated obligations. This way of analyzing the ethical and legal implications of neuroscience has come to be known as "neurorights." Neurorights can be defined as the ethical, legal, social, or natural principles of freedom or entitlement related to a person's cerebral and mental domain; that is, the fundamental normative rules for the protection and preservation of the human brain and mind. Although reflections on neurorights have received ample coverage in the mainstream media and have rapidly become a mainstream topic in the public neuroethics discourse, the frequency of such reflections in the academic literature is still relatively scarce. While the prominence of the neurorights debate in public opinion is crucial to ensure public engagement and democratic participation in deliberative processes on this issue, its relatively sporadic presence in the academic literature poses a risk of semantic-normative ambiguity and conceptual confusion. This risk is exacerbated by the presence of multiple and not always reconcilable terminologies. Several meta-ethical, normative ethical, and legal-philosophical questions need to be solved in order to ensure that neurorights can be used as effective instruments of global neurotechnology governance and be adequately imported into international human rights law. To overcome the shortcomings above, this paper attempts to provide a comprehensive normative-ethical, historical and conceptual analysis of neurorights. In particular, it attempts to (i) reconstruct a history of neurorights and locate these rights in the broader history of idea, (ii) outline a systematic conceptual taxonomy of neurorights, (iii) summarize ongoing policy initiatives related to neurorights, (iv) proactively address some unresolved ethico-legal challenges, and (v) identify priority areas for further academic reflection and policy work in this domain.
Keywords: human rights; neuroethics; neurolaw; neurorights; science policy.
Copyright © 2021 Ienca.
Conflict of interest statement
MI is a member of the Council of the Neurorights Network and a member of the Steering Committee on Neurotechnology of the OECD and has served as an expert advisor to the Council of Europe’s Ad Hoc Committee on Artificial Intelligence on the topic of AI & human rights. He is currently serving as an expert advisor to the Council of Europe’s Committee on Bioethics as part of the Strategic Action Plan on Human Rights and Technologies in Biomedicine.
Similar articles
-
Minding Rights: Mapping Ethical and Legal Foundations of 'Neurorights'.Camb Q Healthc Ethics. 2023 May 15:1-21. doi: 10.1017/S0963180123000245. Online ahead of print. Camb Q Healthc Ethics. 2023. PMID: 37183686
-
Contextual and Cultural Perspectives on Neurorights: Reflections Toward an International Consensus.AJOB Neurosci. 2023 Oct-Dec;14(4):360-368. doi: 10.1080/21507740.2022.2048722. Epub 2022 Mar 27. AJOB Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 35341473
-
Neurorights in History: A Contemporary Review of José M. R. Delgado's "Physical Control of the Mind" (1969) and Elliot S. Valenstein's "Brain Control" (1973).Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Oct 27;15:703308. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.703308. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34776898 Free PMC article.
-
On pharmacological neuroenhancement as part of the new neurorights' pioneering legislation in Chile: a perspective.Front Psychol. 2023 Jul 18;14:1177720. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1177720. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37533709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurorights in the Constitution: from neurotechnology to ethics and politics.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;379(1915):20230098. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0098. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39428886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of media coverage concerning the social implications on three life sciences in Japan during 1991-2020.Front Sociol. 2025 Mar 11;10:1523795. doi: 10.3389/fsoc.2025.1523795. eCollection 2025. Front Sociol. 2025. PMID: 40134518 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotechnologies under the Eye of Bioethics.eNeuro. 2022 Jun 17;9(3):ENEURO.0072-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0072-22.2022. Print 2022 May-Jun. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35697510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Developer perspectives on the ethics of AI-driven neural implants: a qualitative study.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 3;14(1):7880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58535-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38570593 Free PMC article.
-
Self-monitoring of health - user viewpoints on gathering data using consumer health technologies during leisure time.Front Digit Health. 2025 Jun 30;7:1588183. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2025.1588183. eCollection 2025. Front Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40661656 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative review on neuroethical issues in neuroscientific and neuroethical journals.Front Neurosci. 2023 Sep 14;17:1160611. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1160611. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37781239 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alston P. (1984). Conjuring up new human rights: a proposal for quality control. Am. J. Int. Law 78 607–621. 10.2307/2202599 - DOI
-
- Baker L. R. (2000). Persons And Bodies: A Constitution View. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Berlin I. (1969). Two Concepts of Liberty. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
-
- Boire R. G. (2001). On cognitive liberty. J. Cogn. Liberties 2 7–22.
-
- Brandeis L., Warren S. (1890). The right to privacy. Harv. Law Rev. 4 193–220.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources