Herbal Formula SS-1 Increases Tear Secretion for Sjögren's Syndrome
- PMID: 34630072
- PMCID: PMC8498214
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645437
Herbal Formula SS-1 Increases Tear Secretion for Sjögren's Syndrome
Abstract
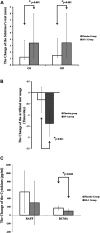
Background: Sjögren's syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease that primarily affects the exocrine glands, leading to glandular dysfunction. The hallmark symptoms of SS are dry eyes and mouth, compromising the quality of life of patients and decreasing their capacity to perform their daily activities. Objective: This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of the herbal formula SS-1 for its potential therapeutic benefits for patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Materials and Methods: The bioactivity profile of SS-1 was determined using four different SS-1 concentrations across 12 human primary cell systems of the BioMAP profile. After that, a randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled trial was performed including 57 patients treated with SS-1 for 28 weeks. Results: Biologically multiplexed activity profiling in cell-based models indicated that SS-1 exerted anti-proliferative activity in B cells and promoted anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activity. In the clinical trial, Schirmer's test results revealed significant improvements in both eyes, with increases of 3.42 mm (95% CI, 2.44-4.41 mm) and 3.45 mm (95% CI, 2.32-4.59 mm), respectively, and a significant reduction in artificial tear use, which was -1.38 times/day, 95% CI, -1.95 to -0.81 times/day. Moreover, the increases in B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) levels were dampened by 53.20% (295.29 versus 555.02 pg/ml) and 58.33% (99.16 versus 169.99 pg/ml), respectively. Conclusion: SS-1 treatment significantly inhibited B-cell maturation antigen. No serious drug-related adverse effects were observed. Oral SS-1 administration may be a complementary treatment for Sjögren's syndrome.
Keywords: Herbal formula; Integrative therapy; SS-1; Sjögren’s syndrome; Xerophthalmia.
Copyright © 2021 Chang, Wu, Lin, Jan Wu, Luo, Hsue, Lan, Pan, Wu, Yu, Wei and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

