Rivaroxaban Modulates TLR4/Myd88/NF-Kβ Signaling Pathway in a Dose-Dependent Manner With Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in an Experimental Model of Depression
- PMID: 34630092
- PMCID: PMC8497790
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.715354
Rivaroxaban Modulates TLR4/Myd88/NF-Kβ Signaling Pathway in a Dose-Dependent Manner With Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in an Experimental Model of Depression
Abstract
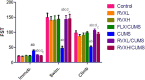
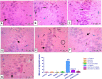
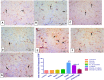
Depression is a common mental illness leading to upset or anxiety, with a high incidence rate in the world. Depression can lead to suicidal thoughts and behavior. The present study aimed to evaluate the effect of the direct oral anticoagulant rivaroxaban (RVX), in the model of depression induced by chronic unpredicted mild stress (CUMS) in rats. Fifty-six male Wister rats were randomly divided into seven experimental groups (8 rats/group); Group 1: Control group given vehicle per oral (p.o.), Group 2: RVXL-control group (received rivaroxaban 20 mg/kg/day, p.o..), Group 3: RVXH-control group (received rivaroxaban 30 mg/kg/day, p.o.), Group 4: chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) group, Group 5: FLX-treated CUMS group (received fluoxetine 10 mg/kg/day, p.o..), Group 6: RVXL-treated CUMS group (received rivaroxaban 20 mg/kg/day, p.o.), and Group 7: RVXH-treated CUMS group (received rivaroxaban 30 mg/kg/day, p.o.). The rats received the drugs from the first day of the experiment and continued till 4 weeks-the duration of the study. The following were measured: monoamine neurotransmitters, malondialdehyde (MDA), total nitrite/nitrate (NOx), reduced glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A). A forced swimming test (FST) was done. Furthermore, histological changes and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoexpression were evaluated. CUMS showed a significant decrease in hypothalamic neurotransmitters, hippocampal GSH, SOD, BNDF, and VEGF-A with a significant increase in hippocampal MDA, NOx, NF-kβ, Myd88, TLR4, TNF-α, and GFAP immunoexpression. RVX showed significant improvement in all parameters (p -value < 0.0001). In conclusion, RVX in a dose-dependent manner possesses potent ameliorative effects against depression by reducing the oxidative stress and inflammatory process, through the regulation of the TLR4/Myd88/NF-kβ signaling pathway.
Keywords: MyD88; NF-kβ; TLR4; depression; rivaroxban.
Copyright © 2021 Abdelzaher, Mohammed, Welson, Batiha, Baty and Abdel-Aziz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Aerobic Exercise Inhibits CUMS-Depressed Mice Hippocampal Inflammatory Response via Activating Hippocampal miR-223/TLR4/MyD88-NF-κB Pathway.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 14;17(8):2676. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082676. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32295141 Free PMC article.
-
Safflower extract improves depression in mice by inhibiting the TLR4-NLRP3 inflammation signaling pathway.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jul;10(7):8015-8023. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1728. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34353086
-
Cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN55212-2 reduces unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive behavior of rats.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jul;9(14):1170. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3143. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34430611 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of geniposide on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice through BTK/TLR4/NF-κB and BDNF/TrkB signaling pathways.Phytother Res. 2021 Feb;35(2):932-945. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6846. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33164233
-
Knockdown of FSTL1 inhibits microglia activation and alleviates depressive-like symptoms through modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in CUMS mice.Exp Neurol. 2022 Jul;353:114060. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.114060. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Exp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35367454
Cited by
-
Antidepressant effects of cherry leaf decoction on a chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model based on the Glu/GABA-Gln metabolic loop.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Dec;37(8):2883-2901. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01081-7. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 36181653
-
Intermedin Reduces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury via JAK2/STAT3.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 24;12:817874. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.817874. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35140609 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Properties of Oral Antithrombotic Therapies in Atherosclerotic Disease and Atrial Fibrillation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 30;12(6):1185. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061185. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rivaroxaban Combined with Atorvastatin Inhibits Acute Pulmonary Embolism by Promoting the Expression of NRF2/NQO1.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Dec;38(6):1271-1287. doi: 10.1007/s10557-023-07479-4. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 37316694
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Effects of Anticoagulant Therapy in Patients with Malignancy.Life (Basel). 2023 Sep 10;13(9):1888. doi: 10.3390/life13091888. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763292 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aladaileh S. H., Abukhalil M. H., Saghir S. A. M., Hanieh H., Alfwuaires M. A., Almaiman A. A., et al. (2019). Galangin Activates Nrf2 Signaling and Attenuates Oxidative Damage, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Biomolecules 9, 346. 10.3390/biom9080346 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Harbi N. O., Imam F., Alharbi M. M., Khan M. R., Qamar W., Afzal M., et al. (2020). Role of Rivaroxaban in Sunitinib-Induced Renal Injuries via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Inflammation through the Tissue Nacrosis Factor-α Induced Nuclear Factor-Κappa B Signaling Pathway in Rats. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 50, 361–370. 10.1007/s11239-020-02123-6 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

