Active Fraction Combination From Liuwei Dihuang Decoction Improves Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Neurogenic Microenvironment in Cranially Irradiated Mice
- PMID: 34630096
- PMCID: PMC8495126
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.717719
Active Fraction Combination From Liuwei Dihuang Decoction Improves Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Neurogenic Microenvironment in Cranially Irradiated Mice
Abstract
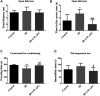
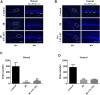
Background: Cranial radiotherapy is clinically used in the treatment of brain tumours; however, the consequent cognitive and emotional dysfunctions seriously impair the life quality of patients. LW-AFC, an active fraction combination extracted from classical traditional Chinese medicine prescription Liuwei Dihuang decoction, can improve cognitive and emotional dysfunctions in many animal models; however, the protective effect of LW-AFC on cranial irradiation-induced cognitive and emotional dysfunctions has not been reported. Recent studies indicate that impairment of adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) and alterations of the neurogenic microenvironment in the hippocampus constitute critical factors in cognitive and emotional dysfunctions following cranial irradiation. Here, our research further investigated the potential protective effects and mechanisms of LW-AFC on cranial irradiation-induced cognitive and emotional dysfunctions in mice. Methods: LW-AFC (1.6 g/kg) was intragastrically administered to mice for 14 days before cranial irradiation (7 Gy γ-ray). AHN was examined by quantifying the number of proliferative neural stem cells and immature neurons in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus. The contextual fear conditioning test, open field test, and tail suspension test were used to assess cognitive and emotional functions in mice. To detect the change of the neurogenic microenvironment, colorimetry and multiplex bead analysis were performed to measure the level of oxidative stress, neurotrophic and growth factors, and inflammation in the hippocampus. Results: LW-AFC exerted beneficial effects on the contextual fear memory, anxiety behaviour, and depression behaviour in irradiated mice. Moreover, LW-AFC increased the number of proliferative neural stem cells and immature neurons in the dorsal hippocampus, displaying a regional specificity of neurogenic response. For the neurogenic microenvironment, LW-AFC significantly increased the contents of superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione, and catalase and decreased the content of malondialdehyde in the hippocampus of irradiated mice, accompanied by the increase in brain-derived neurotrophic factor, insulin-like growth factor-1, and interleukin-4 content. Together, LW-AFC improved cognitive and emotional dysfunctions, promoted AHN preferentially in the dorsal hippocampus, and ameliorated disturbance in the neurogenic microenvironment in irradiated mice. Conclusion: LW-AFC ameliorates cranial irradiation-induced cognitive and emotional dysfunctions, and the underlying mechanisms are mediated by promoting AHN in the dorsal hippocampus and improving the neurogenic microenvironment. LW-AFC might be a promising therapeutic agent to treat cognitive and emotional dysfunctions in patients receiving cranial radiotherapy.
Keywords: LW-AFC; adult hippocampal neurogenesis; cranial irradiation; dorsal hippocampus; neural stem cells; neurogenic microenvironment; traditional Chinese medicine; ventral hippocampus.
Copyright © 2021 Wei, Feng, Zhang, Wang, Chu, Shi, Zhou and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




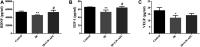
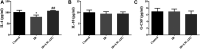
Similar articles
-
Active fraction combination from Liuwei Dihuang decoction (LW-AFC) ameliorates corticosterone-induced long-term potentiation (LTP) impairment in mice in vivo.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 May 23;236:147-154. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30851370
-
LW-AFC, a new formula derived from Liuwei Dihuang decoction, ameliorates behavioral and pathological deterioration via modulating the neuroendocrine-immune system in PrP-hAβPPswe/PS1ΔE9 transgenic mice.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2016 Dec 13;8(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13195-016-0226-6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27964740 Free PMC article.
-
LW-AFC, a new formula from the traditional Chinese medicine Liuwei Dihuang decoction, as a promising therapy for Alzheimer's disease: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms.Adv Pharmacol. 2020;87:159-177. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2019.10.005. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Adv Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32089232 Review.
-
The Effects of LW-AFC on the Hippocampal Transcriptome in Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 Strain, a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(1):227-240. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161079. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28222521
-
Neurogenic hypothesis of positive psychology in stress-induced depression: Adult hippocampal neurogenesis, neuroinflammation, and stress resilience.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Aug;97:107653. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107653. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33915495 Review.
Cited by
-
The Pathogenesis and Prevention Strategies of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury.Cancer Manag Res. 2025 Jul 17;17:1433-1440. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S525791. eCollection 2025. Cancer Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40692945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ablated Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in the Dentate Gyrus of the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus Impairs Hippocampal-Dependent Memory Tasks and Emotion in a Rat Model of Depression.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4352-4368. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03796-9. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38087166
-
Stachyose Alleviates Corticosterone-Induced Long-Term Potentiation Impairment via the Gut-Brain Axis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 10;13:799244. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.799244. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370743 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-altering anterior insular cortex activity affects risk decision-making behavior in mice of different sexes.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Jan 24;17:1094808. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1094808. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36761354 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Irradiation Affects Cellular and Extracellular Components of the Mouse Brain Tissue and Adhesion and Proliferation of Glioblastoma Cells in Experimental System In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 12;22(24):13350. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413350. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948147 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

