Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviate Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma by Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation and Down-Regulating the Differential Expression Proteins
- PMID: 34630102
- PMCID: PMC8493414
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.725953
Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviate Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Asthma by Inhibiting Mast Cell Degranulation and Down-Regulating the Differential Expression Proteins
Abstract
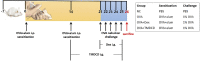
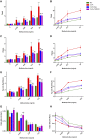
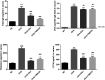
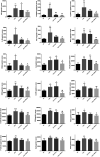
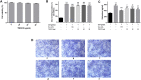
Allergic asthma is a stubborn chronic inflammatory disease, and is considered a co-result of various immune cells, especially mast cells, eosinophils and T lymphocytes. At present, the treatment methods of allergic asthma are limited and the side effects are obvious. Traditional Chinese medicine has been used to treat diseases for thousands of years in China. One such example is the treatment of allergic asthma, which take the characteristics of less adverse reactions and obvious curative effect. Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction (TMDCD) is a traditional Chinese medicine compound for the treatment of allergic asthma optimized from Ma-Xing-Gan-Shi Decoction (MXGSD), which was put forward in Treatise on Febrile Diseases by Zhang Zhongjing in the Eastern Han Dynasty. The compound shows a significant clinical effect, but the mechanism of its influence on the immune system is still unclear. The purpose of this study was to observe whether TMDCD could alleviate the symptoms of ovalbumin (OVA) challenged allergic asthma mice, and to explore its immune regulatory mechanism, especially on mast cell (MC) degranulation. The results showed TMDCD could not only reduce the airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), inflammatory cell infiltration and mucus secretion in the lung tissue of OVA challenged mice, but also decrease the levels of total IgE, OVA-specific IgE, histamine and LTC4 in serum. We found that TMDCD can downregulate the expression of Fractalkine, Tryptase ε, IL-25, CCL19, MCP-1, OX40L, Axl, CCL22, CD30, G-CSF, E-selectin, OPN, CCL5, P-selectin, Gas6, TSLP in OVA challenged mice serum by using mouse cytokines antibody array. It has been reported in some literatures that these differentially expressed proteins are related to the occurrence of allergic asthma, such as tryptase ε, MCP-1, CCL5, etc. can be released by MC. And the results of in vitro experiments showed that TMDCD inhibited the degranulation of RBL-2H3 cells stimulated by DNP-IgE/BSA. Taken together, we made the conclusion that TMDCD could reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells in lung tissue and alleviate airway remodeling in mice with allergic asthma, showed the effects of anti-inflammatory and antiasthmatic. TMDCD could also reduce the levels of IgE, histamine, LTC4, Tryptase ε, and other MC related proteins in the serum of allergic asthma mice, and the in vitro experiments showed that TMDCD could inhibit IgE mediated degranulation and histamine release of RBL-2H3 cells, proved its anti allergic effect.
Keywords: Chinese herbal compound; TMDCD; allergic asthma; differential expression proteins; mast cells.
Copyright © 2021 Qin, Lv, Jiang, Meng, Wang, Cui, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
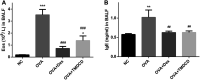


Similar articles
-
Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Airway Inflammations in the Allergic Asthmatic Mice Model by Regulating TLR4-NLRP3 Pathway-Mediated Pyroptosis: A Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Jun 2;17:1613-1630. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S406483. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287697 Free PMC article.
-
Qi-Wei-Du-Qi-Wan and its major constituents exert an anti-asthmatic effect by inhibiting mast cell degranulation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112406. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112406. Epub 2019 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31751647
-
Total glucosides of peony improve ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma by inhibiting mast cell degranulation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Nov 15;244:112136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112136. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31377261
-
Piper nigrum extract ameliorated allergic inflammation through inhibiting Th2/Th17 responses and mast cells activation.Cell Immunol. 2017 Dec;322:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Cell Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29066080
-
Purinergic Signaling in Mast Cell Degranulation and Asthma.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Dec 22;8:947. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00947. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29311944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Asthma via Spatial Regulation of Gut Microbiota and Treg Cell Promotion.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 28;18(5):646. doi: 10.3390/ph18050646. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430465 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-asthmatic Effects of TMDCT Decoction in Eosinophilic Asthma Through Treg/Th17 Balance.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 8;13:819728. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.819728. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35211018 Free PMC article.
-
Tuo-Min-Ding-Chuan Decoction Alleviates Airway Inflammations in the Allergic Asthmatic Mice Model by Regulating TLR4-NLRP3 Pathway-Mediated Pyroptosis: A Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Jun 2;17:1613-1630. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S406483. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287697 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine to improve immune imbalance of asthma: focus on the adjustment of gut microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 1;15:1409128. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1409128. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39411430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bao L. (2017). Study on the Expression of Eosinophil-Related Factors in Allergic Constitution and the Intervention Mechanism of Guominkang. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 141.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

