Dapagliflozin Mediates Plin5/PPARα Signaling Axis to Attenuate Cardiac Hypertrophy
- PMID: 34630108
- PMCID: PMC8495133
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.730623
Dapagliflozin Mediates Plin5/PPARα Signaling Axis to Attenuate Cardiac Hypertrophy
Abstract
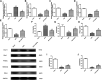
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of dapagliflozin (DAPA), a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor, on relieving cardiac hypertrophy and its potential molecular mechanism. Methods: Cardiac hypertrophy induced by abdominal aortic constriction (AAC) in mice, dapagliflozin were administered in the drinking water at a dose of 25 mg/kg/d for 12 weeks was observed. Echocardiography was used to detect the changes of cardiac function, including LVEF, LVFS, LVEDd, LVEDs, HR and LV mass. Histological morphological changes were evaluated by Masson trichrome staining and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining. The enrichment of differential genes and signal pathways after treatment was analyzed by gene microarray cardiomyocyte hypertrophy was induced by AngII (2 μM) and the protective effect of dapagliflozin (1 μM) was observed in vitro. The morphological changes of myocardial cells were detected by cTnI immunofluorescence staining. ELISA and qRT-PCR assays were performed to detect the expressions levels of cardiac hypertrophy related molecules. Results: After 12 weeks of treatment, DAPA significantly ameliorated cardiac function and inhibited cardiac hypertrophy in AAC-induced mice. In vitro, DAPA significantly inhibited abnormal hypertrophy in AngII-induced cardiacmyocytes. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments have confirmed that DAPA could mediate the Plin5/PPARα signaling axis to play a protective role in inhibiting cardiac hypertrophy. Conclusion: Dapagliflozin activated the Plin5/PPARα signaling axis and exerts a protective effect against cardiac hypertrophy.
Keywords: AngII; Plin5/PPARα signaling; cardiac hypertrophy; dapagliflozin; mice.
Copyright © 2021 Yu, Zhao, Qi, Wei, Li, Li, Zhang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Comment in
-
Commentary: Dapagliflozin Mediates Plin5/PPARα Signaling Axis to Attenuate Cardiac Hypertrophy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 25;13:854593. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.854593. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35548365 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aimo A., Pateras K., Stamatelopoulos K., Bayes-Genis A., Lombardi C. M., Passino C., et al. (2020). Relative Efficacy of Sacubitril-Valsartan, Vericiguat, and SGLT2 Inhibitors in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: a Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 10 (7), 10557–10567. 10.1007/s10557-020-07099-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aistrup G. L., Gupta D. K., Kelly J. E., O'Toole M. J., Nahhas A., Chirayil N., et al. (2013). Inhibition of the Late Sodium Current Slows T-Tubule Disruption during the Progression of Hypertensive Heart Disease in the Rat. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 305 (7), H1068–H1079. 10.1152/ajpheart.00401.2013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouter K. E. C., van Bommel E. J. M., Jansen H., van Harskamp D., Schierbeek H., Ackermans M. T., et al. (2020). The Effect of Dapagliflozin on Apolipoprotein B and Glucose Fluxes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Well-Controlled Plasma LDL Cholesterol. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 22 (6), 988–996. 10.1111/dom.13990 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell F. M., Kozak R., Wagner A., Altarejos J. Y., Dyck J. R., Belke D. D., et al. (2002). A Role for Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha (PPARalpha ) in the Control of Cardiac Malonyl-CoA Levels: Reduced Fatty Acid Oxidation Rates and Increased Glucose Oxidation Rates in the Hearts of Mice Lacking PPARalpha Are Associated with Higher Concentrations of Malonyl-CoA and Reduced Expression of Malonyl-CoA Decarboxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 277 (6), 4098–4103. 10.1074/jbc.M106054200 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

