An Integrative Pharmacology Based Analysis of Refined Liuweiwuling Against Liver Injury: A Novel Component Combination and Hepaprotective Mechanism
- PMID: 34630116
- PMCID: PMC8493075
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.747010
An Integrative Pharmacology Based Analysis of Refined Liuweiwuling Against Liver Injury: A Novel Component Combination and Hepaprotective Mechanism
Abstract
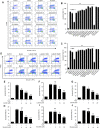
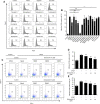
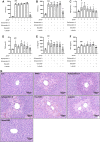
Liver disease is a major cause of illness and death worldwide. In China, liver diseases, primarily alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and viral hepatitis, affect approximately 300 million people, resulting in a major impact on the global burden of liver diseases. The use of Liuweiwuling (LWWL), a traditional Chinese medicine formula, approved by the Chinese Food and Drug Administration for decreasing aminotransferase levels induced by different liver diseases. Our previous study indicated a part of the material basis and mechanisms of LWWL in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis. However, knowledge of the materials and molecular mechanisms of LWWL in the treatment of liver diseases remains limited. Using pharmacokinetic and network pharmacology methods, this study demonstrated that the active components of LWWL were involved in the treatment mechanism against liver diseases and exerted anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammatory effects. Furthermore, esculetin, luteolin, schisandrin A and schisandrin B may play an important role by exerting anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects in vitro. Esculeti and luteolin dose-dependently inhibited H2O2-induced cell apoptosis, and luteolin also inhibited the NF-κB signaling pathway in bone marrow-derived macrophages. schisandrin A and B inhibited the release of ROS in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced acute liver injury in vitro. Moreover, LWWL active ingredients protect against APAP-induced acute liver injury in mice. The four active ingredients may inhibit oxidative stress or inflammation to exert hepatoprotective effect. In conclusion, our results showed that the novel component combination of LWWL can protect against APAP-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting cell apoptosis and exerting anti-inflammatory effects.
Keywords: anti-inflammation; antiapoptosis; component combination; hepatoprotective effect; liuweiwuling; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2021 Gao, Shi, Yao, Ai, Li, Wang, Liu, Dai, Xiao, Zhao, Niu and Bai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liuweiwuling Tablet relieves the inflammatory transformation of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117406. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117406. Epub 2023 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37952733
-
Liuweiwuling tablets attenuate BDL-induced hepatic fibrosis via modulation of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:232-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28864168
-
Protective effects of Liuweiwuling tablets on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jul 9;18(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2276-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29986685 Free PMC article.
-
The combination of Schisandrin C and Luteolin synergistically attenuates hepatitis B virus infection via repressing HBV replication and promoting cGAS-STING pathway activation in macrophages.Chin Med. 2024 Mar 18;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00888-z. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38500179 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin as a potential hepatoprotective drug: Molecular mechanisms and treatment strategies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115464. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115464. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37713990 Review.
Cited by
-
Natural Products for Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Injury: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Dec 1;28(23):7901. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237901. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant and anti‑inflammatory effects of esculin and esculetin (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2024 Apr 12;27(6):248. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12536. eCollection 2024 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38682114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methodology of network pharmacology for research on Chinese herbal medicine against COVID-19: A review.J Integr Med. 2022 Nov;20(6):477-487. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2022.09.004. Epub 2022 Sep 22. J Integr Med. 2022. PMID: 36182651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smilax china L. Polysaccharide Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Protects From Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity via Activating the Nrf2-ARE Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 29;13:888560. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.888560. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35571121 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger receptor A-mediated nanoparticles target M1 macrophages for acute liver injury.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 May;18(3):100813. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100813. Epub 2023 May 9. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37274920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bi H., Li F., Krausz K. W., Qu A., Johnson C. H., Gonzalez F. J. (2013). Targeted Metabolomics of Serum Acylcarnitines Evaluates Hepatoprotective Effect of Wuzhi Tablet (Schisandra Sphenanthera Extract) against Acute Acetaminophen Toxicity. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 985257. 10.1155/2013/985257 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Branch of Hepatobiliary Diseases, CMCA (2020). Expert Consensus on Clinical Application of Liuweiwuling Tablets in the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B. Chin. J. Integrated Traditional West. Med. Liver Dis. 30 (05), 482–485. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2020.05.034 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

