Protective Effects of Lentinan Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mastitis in Mice
- PMID: 34630124
- PMCID: PMC8497700
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.755768
Protective Effects of Lentinan Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mastitis in Mice
Abstract
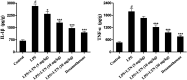
Mastitis is a worldwide production disease in dairy cows, which mainly affects milk yield, causing huge economic losses to dairy farmers. Lentinan is a kind of polysaccharide extracted from Lentinus edodes, which has no toxicity and possesses various pharmacological activities including antibacterial and immunomodulatory effects. Therefore, the anti-inflammatory function of lentinan on LPS-stimulated mastitis was carried out, and the mechanism involved was explored. In vivo, lentinan greatly reduced LPS-stimulated pathological injury, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, and the proinflammatory factor production (TNF-α and IL-1β) in mice. Further study was performed to determine the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway during LPS stimulation. These results suggested that LPS-induced activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway was suppressed by lentinan administration. In vitro, we observed that the mouse mammary epithelial cell (mMEC) viability was not affected by lentinan treatment. As expected, LPS increased the TNF-α and IL-1β protein secretion and the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway that was inhibited by lentinan administration in a dose-dependent manner in mMECs. Conclusively, lentinan exerts the anti-inflammatory function in LPS-stimulated mastitis via inhibiting the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Thus, the results of our study also gave an insight that lentinan may serve as a potential treatment for mastitis.
Keywords: LPS; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; inflammation; lentinan; mastitis.
Copyright © 2021 Yin, Xue, Dai and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Sanguinarine Enhances the Integrity of the Blood-Milk Barrier and Inhibits Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Mastitis.Cells. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3658. doi: 10.3390/cells11223658. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429086 Free PMC article.
-
Myricetin relieves LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting inflammatory response and repairing the blood-milk barrier.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Sep;234(9):16252-16262. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28288. Epub 2019 Feb 11. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30746687
-
Nuciferine alleviates LPS-induced mastitis in mice via suppressing the TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway.Inflamm Res. 2018 Dec;67(11-12):903-911. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1183-2. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 30145653
-
β-elemene attenuates macrophage activation and proinflammatory factor production via crosstalk with Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Fitoterapia. 2018 Jan;124:92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2017.10.015. Epub 2017 Oct 21. Fitoterapia. 2018. PMID: 29066299
-
Morin alleviates LPS-induced mastitis by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT, MAPK, NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathway and protecting the integrity of blood-milk barrier.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jan;78:105972. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105972. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31711938
Cited by
-
Sanguinarine Enhances the Integrity of the Blood-Milk Barrier and Inhibits Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Mastitis.Cells. 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3658. doi: 10.3390/cells11223658. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429086 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochalasin B Mitigates the Inflammatory Response in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mastitis by Suppressing Both the ARPC3/ARPC4-Dependent Cytoskeletal Changes and the Association Between HSP70 and the NLRP3 Inflammasome.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 26;26(7):3029. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073029. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243637 Free PMC article.
-
Danggui Buxue Decoction Alleviates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Mice with Escherichia coli-Induced Mastitis.Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 2;12(3):227. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12030227. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40266913 Free PMC article.
-
The Dectin-1 Receptor Signaling Pathway Mediates the Remyelination Effect of Lentinan through Suppression of Neuroinflammation and Conversion of Microglia.J Immunol Res. 2022 Dec 28;2022:3002304. doi: 10.1155/2022/3002304. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36619719 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonelli M., Donelli D., Firenzuoli F. (2020). “Lentinan for Integrative Cancer Treatment: an Umbrella Review,” in 1st International Electronic Conference on Biomolecules: Natural and Bio-Inspired Therapeutics for Human Diseases. 10.3390/iecbm2020-08733 - DOI
-
- Dai H., Coleman D. N., Hu L., Martinez-Cortés I., Wang M., Parys C., et al. (2019). Methionine and Arginine Supplementation Alter Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Responses during Lipopolysaccharide challenge in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells In Vitro . J. Dairy Sci. 103, 676–689. 10.3168/jds.2019-16631 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

