Circulating MicroRNAs in the Second Trimester From Pregnant Women Who Subsequently Developed Preeclampsia: Potential Candidates as Predictive Biomarkers and Pathway Analysis for Target Genes of miR-204-5p
- PMID: 34630130
- PMCID: PMC8493119
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.678184
Circulating MicroRNAs in the Second Trimester From Pregnant Women Who Subsequently Developed Preeclampsia: Potential Candidates as Predictive Biomarkers and Pathway Analysis for Target Genes of miR-204-5p
Abstract
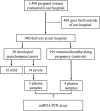
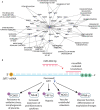
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in the pathophysiology of preeclampsia (PE). However, the expression of circulating miRNAs was not analyzed in the second trimester of pregnancy, a period of major relevance to identify predictive biomarkers for PE. Therefore, we examined the expression profiles of 84 circulating miRNAs using a PCR array in plasma collected between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation from pregnant women, who subsequently developed PE and those who remained healthy during pregnancy, randomly selected from a prospective cohort. Overall, 23 miRNAs had a fold change > 2.0 and were considered to be upregulated in plasma from pregnant women who subsequently developed PE, even before the onset of clinical symptoms of PE. However, only miR-204-5p was statistically significant (P = 0.0082). Experimentally validated interactions for the target genes of miR-204-5p extracted from miRTarBase were used in the gene set functional enrichment analysis to identify Reactome pathways. The network connecting the 37 target genes for miR-204-5p revealed pathways of known pathophysiological relevance during the early development of PE and included key genes related to PE, such as BDNF, MMP-9, MALAT1, TGFBR2, and SIRT1. We further depicted downstream targets of SIRT1 that are related to the vascular endothelial function or implicated in the pathophysiology of PE, namely, FOXO1, NFκB, HIF-1α, NOS3, and PPAR-γ. Our novel findings provide for circulating miRNAs upregulated in the second trimester on plasma from pregnant women who subsequently developed PE that is potentially related to the early development of PE, which may guide further studies focused on the validation of potential predictive biomarkers in PE.
Keywords: biomarkers; gene expression profiling; gene expression regulation; microRNAs; preeclampsia; pregnancy; signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2021 Luizon, Conceição, Viana-Mattioli, Caldeira-Dias, Cavalli and Sandrim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiovascular Disease-Associated MicroRNA Dysregulation during the First Trimester of Gestation in Women with Chronic Hypertension and Normotensive Women Subsequently Developing Gestational Hypertension or Preeclampsia with or without Fetal Growth Restriction.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 25;10(2):256. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020256. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203467 Free PMC article.
-
Early-onset preeclampsia, plasma microRNAs, and endothelial cell function.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May;222(5):497.e1-497.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.11.1286. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 31836544
-
The Prediction of Gestational Hypertension, Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction via the First Trimester Screening of Plasma Exosomal C19MC microRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 18;20(12):2972. doi: 10.3390/ijms20122972. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31216670 Free PMC article.
-
Blood laboratory testing for early prediction of preeclampsia: chasing the finish line or at the starting blocks?Ann Med. 2017 May;49(3):240-253. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2016.1255350. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Ann Med. 2017. PMID: 27791388 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Preeclampsia: Bridging Diagnosis and Treatment.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 15;14(6):2003. doi: 10.3390/jcm14062003. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Review of the Diagnostic and Clinical Utility of Salivary microRNAs in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 29;23(21):13160. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113160. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361944 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in microRNA expression associated with preeclampsia: a systematic review.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025 May 30;58:e13988. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2025e13988. eCollection 2025. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 40465880 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs as Reliable Tumor Biomarkers: Opportunities and Challenges Facing Clinical Application.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2023 Jan;384(1):35-51. doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000896. Epub 2022 Jul 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2023. PMID: 35809898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of altered miRNAs and their targets in placenta accreta.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 3;14:1021640. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1021640. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36936174 Free PMC article.
-
A blood-based miRNA signature for early non-invasive diagnosis of preeclampsia.BMC Med. 2022 Sep 13;20(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02495-x. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 36096786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caldeira-Dias M., Luizon M. R., Deffune E., Tanus-Santos J. E., Freire P. P., Carvalho R. F., et al. . (2018). Preeclamptic plasma stimulates the expression of miRNAs, leading to a decrease in endothelin-1 production in endothelial cells. Pregnancy Hypertens. 12, 75–81. 10.1016/j.preghy.2018.03.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

