Secondhand Smoke Decreased Excitability and Altered Action Potential Characteristics of Cardiac Vagal Neurons in Mice
- PMID: 34630146
- PMCID: PMC8498211
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.727000
Secondhand Smoke Decreased Excitability and Altered Action Potential Characteristics of Cardiac Vagal Neurons in Mice
Abstract
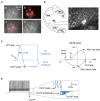
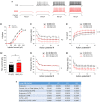
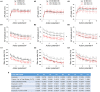
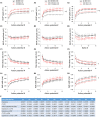
Background: Secondhand smoke (SHS), a major indoor pollutant, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality including arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Exposure to SHS can produce autonomic imbalance, as evidenced by reduced heart rate variability (HRV)-a clinical metric of cardiac vagal regulation. Currently, the mechanisms through which SHS changes the vagal preganglionic neuronal inputs to the heart to produce this remains unknown. Objectives: To characterize the effect of SHS on both the excitability and action potential (AP) characteristics of anatomically identified cardiac vagal neurons (CVNs) in the nucleus ambiguus and examine whether SHS alters small conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channel activity of these CVNs. Methods: Adult male mice were exposed to four weeks of filtered air or SHS (3 mg/m3) 6 h/day, 5 day/week. Using patch-clamp recordings on identified CVNs in brainstem slices, we determined neuronal excitability and AP characteristics with depolarizing step- and ramp-current injections. Results: Four weeks of SHS exposure reduced spiking responses to depolarizing current injections and increased AP voltage threshold in CVNs. Perfusion with apamin (20 nM) magnified these SHS-induced effects, suggesting reduced SK channel activity may serve to minimize the SHS-induced decreases in CVNs excitability. Medium afterhyperpolarization (a measurement of SK channel activity) was smaller in the SHS group, further supporting a lower SK channel activity. AP amplitude, rise rate, fast afterhyperpolarization amplitude (a measurement of voltage-gated channel activity), and decay rate were higher in the SHS group at membrane voltages more positive to 0 mV, suggesting altered inactivation properties of voltage-dependent channels underlying APs. Discussion: SHS exposure reduced neuronal excitability of CVNs with compensatory attenuation of SK channel activity and altered AP characteristics. Neuroplasticity of CVNs could blunt regulatory cardiac vagal signaling and contribute to the cardiovascular consequences associated with SHS exposure, including reduced HRV.
Keywords: SK channel; autonomic function; cardiovascular; environmental tobacco smoke; neuroplasticity; nucleus ambiguus; spiking activity.
Copyright © 2021 Sun, Pan, Karey, Chen, Pinkerton, Wilson and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

