Insomnia Promotes Hepatic Steatosis in Rats Possibly by Mediating Sympathetic Overactivation
- PMID: 34630154
- PMCID: PMC8497715
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.734009
Insomnia Promotes Hepatic Steatosis in Rats Possibly by Mediating Sympathetic Overactivation
Abstract
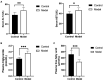
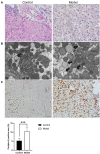
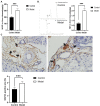
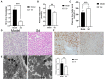
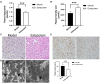
Background: Insomnia is a widespread problem that can lead to the occurrence of other diseases and correlates closely with sympathetic nerve hyperactivation. Obesity-induced hepatic steatosis is mediated by sympathetic overactivation. However, it remains unclear whether insomnia may cause hepatic steatosis. The goal of this study was to preliminarily investigate whether insomnia caused hepatic steatosis in rats via sympathetic hyperactivation. Methods: A total of 32 Sprague-Dawley male rats were divided randomly into four groups: model, sympathetic denervation (Sd), estazolam, and control (eight rats/group). Model group received sustained sleep deprivation using the modified multiple platform method. In the Sd group, rats underwent sleep deprivation after receiving Sd by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). Estazolam group: the rats concurrently received sleep deprivation and treatment with estazolam. The other eight rats housed in cages and kept in a comfortable environment were used as control. Blood samples were obtained for analysis of plasma lipids and hepatic function. Sympathetic hyperactivation-related indexes and hepatic steatosis in liver tissues were tested. Results: Liver enzymes, plasma lipid levels, and hepatic steatosis were elevated in insomnia rats, and sympathetic hyperactivation was found. Insomnia-induced hepatic steatosis was effectively lowered with pharmacological ablation of the hepatic sympathetic nerves. Furthermore, the treatment of insomnia with estazolam inhibited sympathetic activation and reduced hepatic steatosis. Conclusion: Sustained sleep deprivation-induced insomnia promotes hepatic steatosis in rats possibly by mediating sympathetic overactivation.
Keywords: hepatic steatosis; insomnia; lipid droplets; sleep deprivation; sympathetic nerve.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Liang, Lu, Jiang, Aji, Aimulajiang, Sun, Zhang, Zhou, Tang and Wen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Liver sympathetic denervation reverses obesity-induced hepatic steatosis.J Physiol. 2019 Sep;597(17):4565-4580. doi: 10.1113/JP277994. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31278754 Free PMC article.
-
["Governor vessel daoqi method of acupuncture" combined with estazolam for insomnia: a randomized controlled trial].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2018 May 12;38(5):4633-7. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2018.05.003. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2018. PMID: 29797908 Review. Chinese.
-
[Effect of acupuncture and estazolam on episodic memory and sleep structure in patients with chronic insomnia disorder: a randomized controlled trial].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2020 Jul 12;40(7):707-12. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20191208-k0006. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2020. PMID: 32648392 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Foshouningshen decoction improves sleeping via the serotonergic system in a rat model of insomnia].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017 Aug 20;37(8):1116-1120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.08.19. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28801295 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Clinical effectiveness of Tui Na for insomnia compared with estazolam: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2019 Dec;47:102186. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.08.020. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Complement Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31779989
Cited by
-
Hepatic Innervations and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Semin Liver Dis. 2023 May;43(2):149-162. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-57237. Epub 2023 May 8. Semin Liver Dis. 2023. PMID: 37156523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep deprivation-induced sympathetic activation promotes pro-tumoral macrophage phenotype via the ADRB2/KLF4 pathway to facilitate NSCLC metastasis.iScience. 2025 Mar 30;28(5):112321. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112321. eCollection 2025 May 16. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40276761 Free PMC article.
-
Desmosomal Junctions and Connexin-43 Remodeling in High-Pacing-Induced Heart Failure Dogs.Anatol J Cardiol. 2023 Aug 1;27(8):462-471. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2023.2823. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Anatol J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37288855 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep fragmentation exacerbates myocardial ischemia‒reperfusion injury by promoting copper overload in cardiomyocytes.Nat Commun. 2024 May 7;15(1):3834. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48227-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38714741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belenky G., Wesensten N. J., Thorne D. R., Thomas M. L., Sing H. C., Redmond D. P., et al. . (2003). Patterns of performance degradation and restoration during sleep restriction and subsequent recovery: a sleep dose-response study. J. Sleep Res. 12, 1–12. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2869.2003.00337.x, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

