N6 -Methyladenosine and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 34630412
- PMCID: PMC8498590
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731842
N6 -Methyladenosine and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA), one of the most common autoimmune diseases, is characterized by immune cell infiltration, fibroblast-like synovial cell hyperproliferation, and cartilage and bone destruction. To date, numerous studies have demonstrated that immune cells are one of the key targets for the treatment of RA. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most common internal modification to eukaryotic mRNA, which is involved in the splicing, stability, export, and degradation of RNA metabolism. m6A methylated-related genes are divided into writers, erasers, and readers, and they are critical for the regulation of cell life. They play a significant role in various biological processes, such as virus replication and cell differentiation by controlling gene expression. Furthermore, a growing number of studies have indicated that m6A is associated with the occurrence of numerous diseases, such as lung cancer, bladder cancer, gastric cancer, acute myeloid leukemia, and hepatocellular carcinoma. In this review, we summarize the history of m6A research and recent progress on RA research concerning m6A enzymes. The relationship between m6A enzymes, immune cells, and RA suggests that m6A modification offers evidence for the pathogenesis of RA, which will help in the development of new therapies for RA.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; autoimmune disease; cancers; immune cells; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Li, Wu, Yin, Huang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
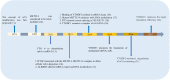
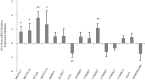
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

