Effect of Pr in CO2 Methanation Ru/CeO2 Catalysts
- PMID: 34630817
- PMCID: PMC8494384
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c03539
Effect of Pr in CO2 Methanation Ru/CeO2 Catalysts
Abstract
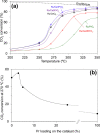
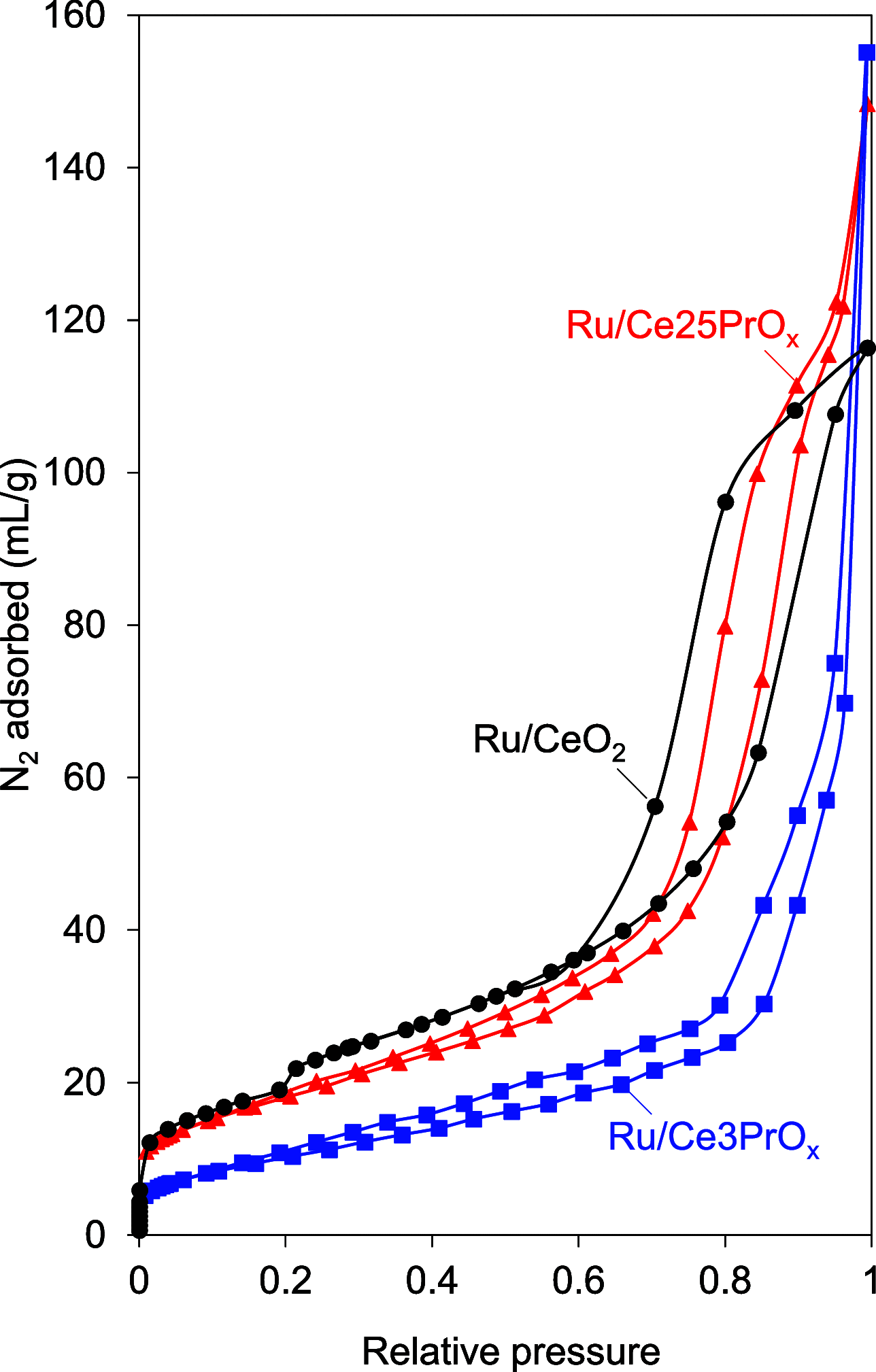
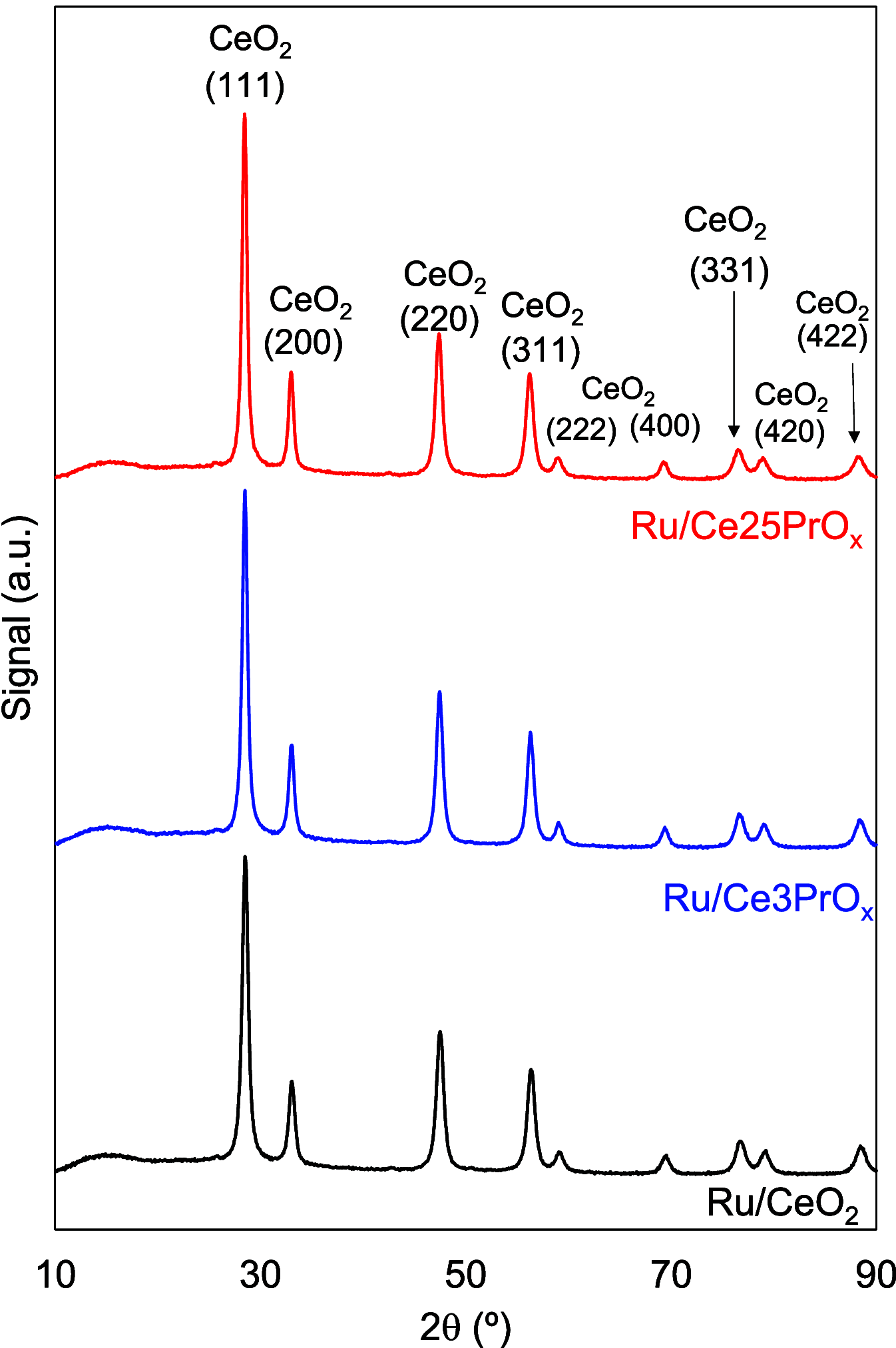
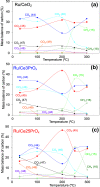
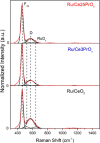
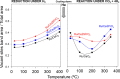
CO2 methanation has been studied with Pr-doped Ru/CeO2 catalysts, and a dual effect of Pr has been observed. For low Pr content (i.e., 3 wt %) a positive effect in oxygen mobility prevails, while for high Pr doping (i.e., 25 wt %) a negative effect in the Ru-CeO2 interaction is more relevant. Isotopic experiments evidenced that Pr hinders the dissociation of CO2, which takes place at the Ru-CeO2 interface. However, once the temperature is high enough (200 °C), Pr improves the oxygen mobility in the CeO2 support, and this enhances CO2 dissociation because the oxygen atoms left are delivered faster to the support sink and the dissociation sites at the interface are cleaned up faster. In situ Raman spectroscopy experiments confirmed that Pr improves the creation of oxygen vacancies on the ceria lattice but hinders their reoxidation by CO2, and both opposite effects reach an optimum balance for 3 wt % Pr doping. In addition, in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) experiments showed that Pr doping, regardless of the amount, decreases the population of surface carbon species created on the catalysts surface upon CO2 chemisorption under methanation reaction conditions, affecting both productive reaction intermediates (formates and carbonyls) and unproductive carbonates.
© 2021 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Pereira-Hernández X. I.; De La Riva A.; Muravev V.; Kunwar D.; Xiong H.; Sudduth B.; Engelhard M.; Kovarik L.; Hensen E. J. M.; Wang Y.; et al. Tuning Pt-CeO2 interactions by high-temperature vapor-phase synthesis for improved reducibility of lattice oxygen. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1358.10.1038/s41467-019-09308-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Trovarelli A. Catalytic Properties of Ceria and CeO2-Containing Materials. Catal. Rev.: Sci. Eng. 1996, 38, 439–520. 10.1080/01614949608006464. - DOI
-
- Atribak I.; Bueno-López A.; García-García A. Role of yttrium loading in the physico-chemical properties and soot combustion activity of ceria and ceria–zirconia catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2009, 300, 103–110. 10.1016/j.molcata.2008.10.043. - DOI
-
- Ke J.; Xiao J.-W.; Zhu W.; Liu H.; Si R.; Zhang Y.-W.; Yan C.-H. Dopant-Induced Modification of Active Site Structure and Surface Bonding Mode for High-Performance Nanocatalysts: CO Oxidation on Capping-free (110)-oriented CeO2:Ln (Ln = La–Lu) Nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15191–15200. 10.1021/ja407616p. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
