Is there a volume threshold of brain metastases for Linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy?
- PMID: 34631232
- PMCID: PMC8492046
Is there a volume threshold of brain metastases for Linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy?
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate whether there is a volume threshold in target volume of brain metastases below which a small cone size and sharp penumbra in Gamma Knife (GK) may provide improved plan quality when compared to Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
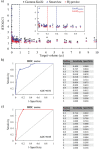
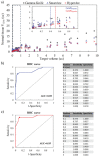
Methods: For patients treated on GK SRS for brain metastases in 2018-2019 in our institution, 121 patients with two and three targets were identified. Twenty-six patients with two or three brain metastases (total of 76 lesions) were selected for this study. Two VMAT plans, SmartArc (Pinnacle) and HyperArc (Eclipse), were generated retrospectively for each patient. Plan quality was evaluated based on RTOG conformity index (CI), Paddick gradient index (GI), normal tissue (NT) V12Gy and V4.5Gy. By using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for both VMAT plans (SmartArc and HyperArc) and metrics of RTOG CI and NT V12Gy, we compared GK plans to SmartArc and HyperArc plans separately to determine the threshold volume.
Results: For SmartArc plans, both ROC curve analyses showed a threshold volume of 0.4 cc for both CI and NT V12Gy. For HyperArc plans, the threshold volumes were 0.2 cc for the CI and 0.5 cc for NT V12Gy. GK plans produced improved dose distribution compared to VMAT for targets ≤0.4 cc, but HyperArc was found to have competing results with GK in terms of CI and NT V12Gy. For targets > 0.4 cc, both SmartArc and HyperArc showed better plan quality when compared to the GK plans.
Conclusions: Target volumes ≤0.4 cc may require a small cone size and sharp penumbra in GK while for target volumes >0.4 cc, VMAT-based SRS can provide improved overall plan quality and faster treatment delivery.
Keywords: Gamma Knife; Linac SRS; VMAT; brain metastases; plan quality; radiosurgery.
© 2021 Old City Publishing, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ declaration of potential conflicts of interest Dr. Neyman reports personal fees from Elekta AB, outside the submitted work. Dr. Chao reports personal fees from Varian Medical Systems, outside the submitted work. Dr. Suh reports personal fees from Philips, other from Neutron Therapeutics, personal fees from Novocure, outside the submitted work. Dr. Xia reports grants from AVO, during the conduct of the study; grants from Philips, outside the submitted work. Other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multi-Institutional Dosimetric Evaluation of Modern Day Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) Treatment Options for Multiple Brain Metastases.Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 7;9:483. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00483. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31231614 Free PMC article.
-
Direct dosimetric comparison of linear accelerator vs. Gamma Knife fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (fSRT) of large brain tumors.Med Dosim. 2023 Spring;48(1):31-36. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2022.09.006. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Med Dosim. 2023. PMID: 36503990
-
Assessment of single isocenter linear accelerator radiosurgery for metastases and base of skull lesions.Phys Med. 2021 Jan;81:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2020.11.011. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Phys Med. 2021. PMID: 33278764
-
Insights into the dosimetric and geometric characteristics of stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 9;19(8):e0307088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307088. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39121064 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Radiation Therapy of Single Brain Metastases: A Literature Review of Dosimetric Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 2;15(15):3937. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153937. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A new conformity and dose gradient distance measure for stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastasis.J Radiosurg SBRT. 2022;8(1):27-36. J Radiosurg SBRT. 2022. PMID: 35387404 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive assessment of proton plans with three different beam delivery systems for multiple brain metastases.J Radiosurg SBRT. 2024;9(2):145-156. J Radiosurg SBRT. 2024. PMID: 39087064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsao M, Xu W, Sahgal A. A meta-analysis evaluating stereotactic radiosurgery, whole-brain radiotherapy, or both for patients presenting with a limited number of brain metastases. Cancer. 2012;118(9):2486-2493. - PubMed
-
- Mayo CS, Ding L, Addesa A, Kadish S, Fitzgerald TJ, Moser R. Initial experience with volumetric IMRT (RapidArc) for intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;78(5):1457-1466. - PubMed
-
- Clark GM, Popple RA, Prendergast BM, Spencer SA, Thomas EM, Stewart JG, Guthrie BL, Markert JM, Fiveash JB. Plan quality and treatment planning technique for single isocenter cranial radiosurgery with volumetric modulated arc therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2012;2(4):306-313. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
