miR-320a induces pancreatic β cells dysfunction in diabetes by inhibiting MafF
- PMID: 34631276
- PMCID: PMC8479292
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.08.027
miR-320a induces pancreatic β cells dysfunction in diabetes by inhibiting MafF
Abstract
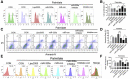
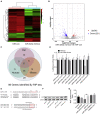
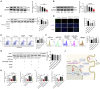
A variety of studies indicate that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in diabetes. However, the direct role of miR-320a in the pathophysiology of pancreatic β cells under diabetes mellitus remains unclear. In the current study, islet transplantation and hyperglycemic clamp assays were performed in miR-320a transgenic mice to explore the effects of miR-320a on pancreatic β cells in vivo. Meanwhile, β cell-specific overexpression or inhibition of miR-320a was delivered by adeno-associated virus (AAV8). In vitro, overexpression or downregulation of miR-320a was introduced in cultured rat islet tumor cells (INS1). RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing (RIP-Seq), luciferase reporter assay, and western blotting were performed to identify the target genes. Results showed that miR-320a was increased in the pancreatic β cells from high-fat-diet (HFD)-treated mice. Overexpression of miR-320a could not only deteriorate the HFD-induced pancreatic islet dysfunction, but also initiate pancreatic islet dysfunction spontaneously in vivo. Meanwhile, miR-320a increased the ROS level, inhibited proliferation, and induced apoptosis of cultured β cells in vitro. Finally, we identified that MafF was the target of miR-320a that responsible for the dysfunction of pancreatic β cells. Our data suggested that miR-320a could damage the pancreatic β cells directly and might be a potential therapeutic target of diabetes.
Keywords: MafF; diabetes; miRNA; pancreatic islet; β cells.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Dennis J.M., Shields B.M., Henley W.E., Jones A.G., Hattersley A.T. Disease progression and treatment response in data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes compared with models based on simple clinical features: an analysis using clinical trial data. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7:442–451. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye B., Alebel A., Gebrie A., Zegeye A., Tesema Leshargie C., Ferede A., Abera H., Alam K. Diabetes mellitus and its association with hypertension in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019;156:107838. - PubMed
-
- Saltiel A.R., Kahn C.R. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001;414:799–806. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(Suppl 1):S81–S90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

