Machine learning in orthopaedic surgery
- PMID: 34631452
- PMCID: PMC8472446
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v12.i9.685
Machine learning in orthopaedic surgery
Abstract
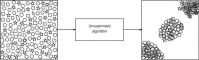
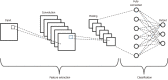
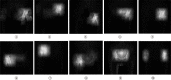
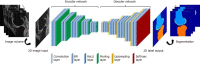
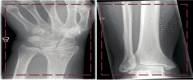
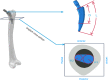
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in orthopaedic surgery has gained mass interest over the last decade or so. In prior studies, researchers have demonstrated that machine learning in orthopaedics can be used for different applications such as fracture detection, bone tumor diagnosis, detecting hip implant mechanical loosening, and grading osteoarthritis. As time goes on, the utility of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, such as deep learning, continues to grow and expand in orthopaedic surgery. The purpose of this review is to provide an understanding of the concepts of machine learning and a background of current and future orthopaedic applications of machine learning in risk assessment, outcomes assessment, imaging, and basic science fields. In most cases, machine learning has proven to be just as effective, if not more effective, than prior methods such as logistic regression in assessment and prediction. With the help of deep learning algorithms, such as artificial neural networks and convolutional neural networks, artificial intelligence in orthopaedics has been able to improve diagnostic accuracy and speed, flag the most critical and urgent patients for immediate attention, reduce the amount of human error, reduce the strain on medical professionals, and improve care. Because machine learning has shown diagnostic and prognostic uses in orthopaedic surgery, physicians should continue to research these techniques and be trained to use these methods effectively in order to improve orthopaedic treatment.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Machine learning; Orthopaedic surgery; Supervised learning; Unsupervised learning.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence in spine care: current applications and future utility.Eur Spine J. 2022 Aug;31(8):2057-2081. doi: 10.1007/s00586-022-07176-0. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Eur Spine J. 2022. PMID: 35347425 Review.
-
Machine learning/artificial intelligence in sports medicine: state of the art and future directions.J ISAKOS. 2024 Aug;9(4):635-644. doi: 10.1016/j.jisako.2024.01.013. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J ISAKOS. 2024. PMID: 38336099 Review.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Pathology: The Present Landscape of Supervised Methods.Acad Pathol. 2019 Sep 3;6:2374289519873088. doi: 10.1177/2374289519873088. eCollection 2019 Jan-Dec. Acad Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31523704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Surgeon's Guide to Understanding Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Studies in Orthopaedic Surgery.Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022 Apr;15(2):121-132. doi: 10.1007/s12178-022-09738-7. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022. PMID: 35141847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in medical imaging of the liver.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb 14;25(6):672-682. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i6.672. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30783371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence Image Recognition System for Preventing Wrong-Site Upper Limb Surgery.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Dec 14;13(24):3667. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13243667. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38132251 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer learning-based ensemble convolutional neural network for accelerated diagnosis of foot fractures.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023 Mar;46(1):265-277. doi: 10.1007/s13246-023-01215-w. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 36625995
-
[Artificial intelligence and novel approaches for treatment of non-union in bone : From established standard methods in medicine up to novel fields of research].Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2022 Aug;125(8):611-618. doi: 10.1007/s00113-022-01202-y. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35810261 Review. German.
-
Emerging Applications of Deep Learning in Bone Tumors: Current Advances and Challenges.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 19;12:908873. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.908873. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35928860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The value of machine learning technology and artificial intelligence to enhance patient safety in spine surgery: a review.Patient Saf Surg. 2024 Mar 25;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13037-024-00393-0. Patient Saf Surg. 2024. PMID: 38528562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miller DD, Brown EW. Artificial Intelligence in Medical Practice: The Question to the Answer? Am J Med. 2018;131:129–133. - PubMed
-
- Borjali A, Chen AF, Muratoglu OK, Morid MA, Varadarajan KM. Deep Learning in Orthopedics: How Do We Build Trust in the Machine? Healthcare Transformat . 2020
-
- Topol E. Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again. Basic Books, 2019.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

