Melatonin increases 5-flurouracil-mediated apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through enhancing oxidative stress and downregulating survivin and XIAP
- PMID: 34631487
- PMCID: PMC8494259
- DOI: 10.34172/bi.2021.36
Melatonin increases 5-flurouracil-mediated apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through enhancing oxidative stress and downregulating survivin and XIAP
Abstract
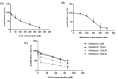
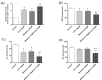
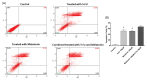
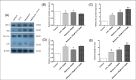
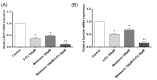
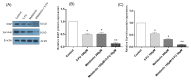
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most lethal human malignancies with a global alarming rate of incidence. The development of resistance against common chemotherapeutics such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) remains a big burden for CRC therapy. Therefore, we investigated the effects of melatonin on the increasing 5-FU- mediated apoptosis and its underlying mechanism in SW-480 CRC cell line. Methods: The effects of melatonin and 5- FU, alone or in combination, on cell proliferation were evaluated using an MTT assay. Further, Annexin-V Flow cytometry was used for determining the effects of melatonin and 5-FU on the apoptosis of SW-480 cell lines. The expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2, pro-caspase-3/activated caspase 3, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (XIAP), and survivin were measured after 48 hours incubation with drugs. Cellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), catalase, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase were also evaluated. Results: Melatonin and 5-FU significantly decreased the cell proliferation of SW-480 cells. Combination of 5-FU with melatonin significantly decreased the IC50 value of 5-FU from 100 μM to 50 μM. Moreover, combination therapy increased intracellular levels of ROS and suppressed antioxidant enzymatic activities (P < 0.05). Treatment with either melatonin or 5-FU resulted in the induction of apoptosis in comparison to control (P > 0.05). XIAP and survivin expression levels potently decreased after combination treatment with melatonin and 5-FU (P < 0.05). Conclusion: We demonstrated that melatonin exerts a reversing effect on the resistance to apoptosis by targeting oxidative stress, XIAP and survivin in CRC cells. Therefore, more studies need for better understanding of underlying mechanisms for beneficial effects of combination of melatonin and 5-FU.
Keywords: 5-FU; Colorectal cancer; Melatonin; Oxidative stress; Survivin; XIAP.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Similar articles
-
The mechanisms and roles of melatonin in gastrointestinal cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 15;12:1066698. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1066698. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36591447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role and mechanism research on reversal of 5-fluorouracil resistance by epigallocatechin gallate in gastric cancer drug-resistance cells lines SGC-7901/5-FU].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Oct 25;19(10):1170-1175. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27781257 Chinese.
-
Gypenosides Synergistically Enhances the Anti-Tumor Effect of 5-Fluorouracil on Colorectal Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo: A Role for Oxidative Stress-Mediated DNA Damage and p53 Activation.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 14;10(9):e0137888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137888. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26368019 Free PMC article.
-
[X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) and Survivin suppression on human pancreatic cancer cells Panc-1 proliferation and chemosensitivety].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Apr 18;45(2):242-9. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 23591345 Chinese.
-
A novel coordination complex of platinum (PT) induces cell death in colorectal cancer by altering redox balance and modulating MAPK pathway.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jul 23;20(1):685. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07165-w. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32703189 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The mechanisms and roles of melatonin in gastrointestinal cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 15;12:1066698. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1066698. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36591447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring potential additive effects of 5-fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and coenzyme Q10 triple therapy on colon cancer cells in relation to glycolysis and redox status modulation.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2025 Mar 10;37(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s43046-025-00261-7. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2025. PMID: 40059278
-
Melatonin Potentiates Sensitivity to 5-Fluorouracil in Gastric Cancer Cells by Upregulating Autophagy and Downregulating Myosin Light-Chain Kinase.J Cancer. 2023 Aug 21;14(14):2608-2618. doi: 10.7150/jca.85353. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37779875 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin: A Potential Regulator of DNA Methylation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 May 25;12(6):1155. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061155. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thymoquinone Increases the Sensitivity of SW-480 Colon Cancer Cells to 5-Fluorouracil.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jul 9;2024:6231095. doi: 10.1155/2024/6231095. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39015603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Macrae FA. Colorectal cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, and protective factors. 2016. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/colorectal-cancer-epidemiology-risk-fa....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials