Stereotactic and Robotic Minimally Invasive Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34631539
- PMCID: PMC8495244
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.713685
Stereotactic and Robotic Minimally Invasive Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Stereotactic navigation techniques aim to enhance treatment precision and safety in minimally invasive thermal ablation of liver tumors. We qualitatively reviewed and quantitatively summarized the available literature on procedural and clinical outcomes after stereotactic navigated ablation of malignant liver tumors.
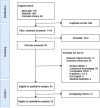
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed on procedural and clinical outcomes when using stereotactic or robotic navigation for laparoscopic or percutaneous thermal ablation. The online databases Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched. Endpoints included targeting accuracy, procedural efficiency, and treatment efficacy outcomes. Meta-analysis including subgroup analyses was performed.
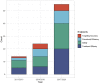
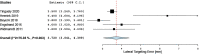
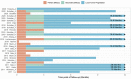
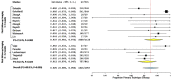
Results: Thirty-four studies (two randomized controlled trials, three prospective cohort studies, 29 case series) were qualitatively analyzed, and 22 studies were included for meta-analysis. Weighted average lateral targeting error was 3.7 mm (CI 3.2, 4.2), with all four comparative studies showing enhanced targeting accuracy compared to free-hand targeting. Weighted average overall complications, major complications, and mortality were 11.4% (6.7, 16.1), 3.4% (2.1, 5.1), and 0.8% (0.5, 1.3). Pooled estimates of primary technique efficacy were 94% (89, 97) if assessed at 1-6 weeks and 90% (87, 93) if assessed at 6-12 weeks post ablation, with remaining between-study heterogeneity. Primary technique efficacy was significantly enhanced in stereotactic vs. free-hand targeting, with odds ratio (OR) of 1.9 (1.2, 3.2) (n = 6 studies).
Conclusions: Advances in stereotactic navigation technologies allow highly precise and safe tumor targeting, leading to enhanced primary treatment efficacy. The use of varying definitions and terminology of safety and efficacy limits comparability among studies, highlighting the crucial need for further standardization of follow-up definitions.
Keywords: ablation techniques; computer-assisted therapies; liver neoplasms; minimally invasive surgical procedures; stereotaxic techniques.
Copyright © 2021 Tinguely, Paolucci, Ruiter, Weber, de Jong, Candinas, Freedman and Engstrand.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Robotic Assistance in Percutaneous Liver Ablation Therapies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ann Surg Open. 2024 Mar 26;5(2):e406. doi: 10.1097/AS9.0000000000000406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Ann Surg Open. 2024. PMID: 38911657 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Image-Guided Microwave Ablation for Malignant Liver Tumors-A Multivariable Accuracy and Efficacy Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Jun 10;10:842. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00842. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32587826 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic CT-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of Liver Tumors With the Use of High-Frequency Jet Ventilation: An Accuracy and Procedural Safety Study.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017 Jan;208(1):193-200. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.15803. Epub 2016 Oct 20. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017. PMID: 27762601 Clinical Trial.
-
Democratization in abdominal ablation therapies: The impact of percutaneous robotic assistance on accuracy-A systematic review.J Robot Surg. 2025 Jan 17;19(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s11701-024-02158-4. J Robot Surg. 2025. PMID: 39821378
-
Stereotactic Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors: 3D Planning, Multiple Needle Approach, and Intraprocedural Image Fusion Are the Key to Success-A Narrative Review.Biology (Basel). 2021 Jul 10;10(7):644. doi: 10.3390/biology10070644. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Volumetric Quantitative Ablation Margins for Assessment of Ablation Completeness in Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 10;11:623098. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.623098. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33777768 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Ablative Techniques in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Indications and Outcomes.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 31;11(4):1062. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041062. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic Percutaneous Electrochemotherapy as a New Minimal Invasive Treatment Modality for Primary and Secondary Liver Malignancies.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 17;12(12):2870. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122870. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767776 Free PMC article.
-
Image-based computer modeling assessment of microwave ablation for treatment of adrenal tumors.Int J Hyperthermia. 2022;39(1):1264-1275. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2125590. Int J Hyperthermia. 2022. PMID: 36137605 Free PMC article.
-
Image-guided percutaneous ablation for lung malignancies.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 10;12:1020296. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1020296. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36439490 Free PMC article. Review.

