High Expression of Complement Component C7 Indicates Poor Prognosis of Breast Cancer and Is Insensitive to Taxane-Anthracycline Chemotherapy
- PMID: 34631552
- PMCID: PMC8497743
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.724250
High Expression of Complement Component C7 Indicates Poor Prognosis of Breast Cancer and Is Insensitive to Taxane-Anthracycline Chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide. However, the well-known biomarkers are not enough to meet the needs of precision medicine. Novel targets are desirable and highly valuable for improved patient survival. In this regard, we identified complement component C7 as one of the candidates based on data from the OCOMINE database.
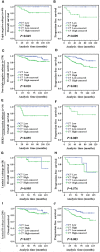
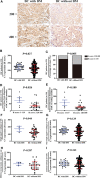
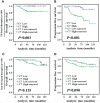
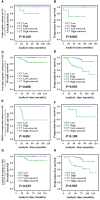
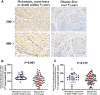
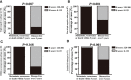
Methods: C7 expression was examined by immunohistochemistry in 331 cases of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), 45 cases of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), and 52 cases of non-neoplastic tissues adjacent to tumor. Then, C7 expression was further confirmed by Western blot analysis based on IDC specimens and non-neoplastic breast specimens. The relationship between the C7 expression and prognosis of breast cancer patients was analyzed in order to investigate the function of C7 in breast cancer patients. Meanwhile, we also analyzed the relationship between the C7 expression and prognosis of 149 patients treated with conventional TE (taxane and anthracycline)-based chemotherapy. Then, a cohort of patients (22 cases) treated with TE neoadjuvant chemotherapy was used to further confirm the relationship between the C7 expression and TE-based chemosensitivity.
Results: In our present study, we reported for the first time that C7 was an independent prognostic factor of breast cancer and C7 expression of IDC tissues was higher than non-neoplastic tissues adjacent to tumor and DCIS. In a cohort of 331 IDC patients, high expression of C7 indicated poor prognosis especially in the triple negative subtype and luminal B subtype. Furthermore, C7 was also a promoting factor for triple negative subtype patients to develop bone metastasis. Meanwhile, we provided the first evidence that patients with high C7 expression were insensitive to TE (taxane and anthracycline)-based chemotherapy by analyzing a cohort of 149 patients treated with TE-based chemotherapy and another cohort of 22 patients treated with TE neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Conclusions: In summary, high expression of C7 may promote breast cancer development and might be insensitive to TE-based chemotherapy. Our present study laid a foundation to help clinicians improve the identification of patients for TE-based chemotherapy by C7 in the era of precision medicine.
Keywords: C7; TE chemotherapy; bone metastasis; breast cancer; prognosis.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Zhao, Liu, Fu, Gu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Low expression of BMPRIB indicates poor prognosis of breast cancer and is insensitive to taxane-anthracycline chemotherapy.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4770-84. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6613. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26684357 Free PMC article.
-
Responsiveness of adjacent ductal carcinoma in situ and changes in HER2 status after neoadjuvant chemotherapy/trastuzumab treatment in early breast cancer--results from the GeparQuattro study (GBG 40).Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(3):863-70. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1621-0. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21667238
-
Anterior Gradient 3 Promotes Breast Cancer Development and Chemotherapy Response.Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan;52(1):218-245. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.217. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 31291711 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of ductal carcinoma in situ on the outcome of invasive breast cancer. A prospective cohort study.Int J Surg. 2019 Mar;63:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.01.016. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Int J Surg. 2019. PMID: 30738200
-
Identification of biology-based breast cancer types with distinct predictive and prognostic features: role of steroid hormone and HER2 receptor expression in patients treated with neoadjuvant anthracycline/taxane-based chemotherapy.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R69. doi: 10.1186/bcr2363. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19758440 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Complement protein expression changes in various conditions of breast cancer: in-silico analyses-experimental research.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jul 17;86(9):5152-5161. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002216. eCollection 2024 Sep. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39239051 Free PMC article.
-
Sialic acid metabolism-based classification reveals novel metabolic subtypes with distinct characteristics of tumor microenvironment and clinical outcomes in gastric cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Feb 22;25(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03695-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 39987095 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison Study of Small Extracellular Vesicle Isolation Methods for Profiling Protein Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Liquid Biopsies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 23;24(20):15462. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015462. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895140 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the diversity of cancer-associated fibroblasts: insights into mechanisms of drug resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 16;12:1403122. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1403122. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38818409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics and network biology approach to identifying type 2 diabetes genes and pathways that influence the progression of breast cancer.Heliyon. 2023 May 12;9(5):e16151. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16151. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37234659 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

