Pediatric COVID-19: Report From Indonesian Pediatric Society Data Registry
- PMID: 34631619
- PMCID: PMC8495320
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.716898
Pediatric COVID-19: Report From Indonesian Pediatric Society Data Registry
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum on: Pediatric COVID-19: Report from Indonesian pediatric society data registry.Front Pediatr. 2022 Oct 19;10:1024699. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.1024699. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36340732 Free PMC article.
Abstract
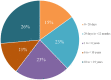
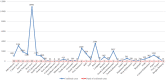
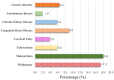
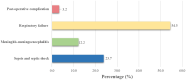
Background: Indonesia has a high number of COVID-19 cases and mortalities relative to not only among the Asia Pacific region but the world. Children were thought to be less affected by the virus compared to adults. Most of the public data reported combined data between adults and children. The Indonesian Pediatric Society (IPS) was involved in the COVID-19 response, especially in the area of child health. One of IPS's activities is collecting data registries from each of their chapters to provide a better understanding of COVID-19 in children. Objective: The objective of this study was to share the data of suspected and confirmed COVID-19 cases in children from IPS's COVID-19 data registry. Method: This is a retrospective study from the IPS's COVID-19 registry data. We collected the data of COVID-19 in children during March to December 2020 from each of the IPS chapters. We analyzed the prevalence, case fatality rate (CFR), age groups, diagnosis, and comorbidities of the children diagnosed with COVID-19. Result: As of December 21, 2020, there were 35,506 suspected cases of children with COVID-19. In total, there were 522 deaths, with a case fatality ratio (CFR) of 1.4. There were 37,706 confirmed cases with 175 fatalities (CFR 0.46). The highest mortality in confirmed COVID-19 cases was from children ages 10-18 years (42 out of 159 cases: 26%). The most common comorbidity and diagnosis found were malignancy (17.3%) and respiratory failure (54.5%). Conclusion: The CFR of confirmed COVID-19 cases in children in Indonesia is high and should be a major public concern.
Keywords: COVID-19; Indonesia; children; comorbidities; mortality.
Copyright © 2021 Pudjiadi, Putri, Sjakti, Yanuarso, Gunardi, Roeslani, Pasaribu, Nurmalia, Sambo, Ugrasena, Soeroso, Firman, Muryawan, Setyanto, Citraresmi, Effendi, Habibah, Octaviantie, Utami, Prawira, Kaswandani, Alam, Kadafi and Pulungan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Situation Reports. (2020). Available online at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... (accessed 22 January, 2021).
-
- Satuan Tugas Penanganan COVID-19 . (2020). Peta Sebaran. Available online at: https://covid19.go.id/peta-sebaran (accessed 28 December, 2020).
-
- Worldometer . Coronavirus Update (Live): 35,437,409 Cases and 1,042,343 Deaths From COVID-19 Virus Pandemic – Worldometer. (2020). Available online at: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed 22 January, 2021).
-
- Nurbaiti A, Syakriah A. Indonesia Reports Higher COVID-19 Death Rate Among Children Than United States. (2020). Available online at: https://www.thejakartapost.com/news/2020/09/03/indonesia-reports-higher-... (accessed 22 January, 2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials