X-Chromosome Inactivation and Autosomal Random Monoallelic Expression as "Faux Amis"
- PMID: 34631717
- PMCID: PMC8495168
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.740937
X-Chromosome Inactivation and Autosomal Random Monoallelic Expression as "Faux Amis"
Abstract
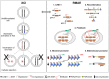
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) and random monoallelic expression of autosomal genes (RMAE) are two paradigms of gene expression regulation where, at the single cell level, genes can be expressed from either the maternal or paternal alleles. X-chromosome inactivation takes place in female marsupial and placental mammals, while RMAE has been described in mammals and also other species. Although the outcome of both processes results in random monoallelic expression and mosaicism at the cellular level, there are many important differences. We provide here a brief sketch of the history behind the discovery of XCI and RMAE. Moreover, we review some of the distinctive features of these two phenomena, with respect to when in development they are established, their roles in dosage compensation and cellular phenotypic diversity, and the molecular mechanisms underlying their initiation and stability.
Keywords: LINE-1 elements; X-chromosome inactivation; cellular diversity; dosage compensation; epigenetic silencing; random monoallelic expression; stochasticity.
Copyright © 2021 Barreto, Kubasova, Alves-Pereira and Gendrel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Random monoallelic expression of genes on autosomes: Parallels with X-chromosome inactivation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27101886 Review.
-
Dosage compensation in mammals: fine-tuning the expression of the X chromosome.Genes Dev. 2006 Jul 15;20(14):1848-67. doi: 10.1101/gad.1422906. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16847345 Review.
-
Bovine mammary gland X chromosome inactivation.J Dairy Sci. 2017 Jul;100(7):5491-5500. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-12490. Epub 2017 May 3. J Dairy Sci. 2017. PMID: 28477999
-
Origin and evolution of X chromosome inactivation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012 Jun;24(3):397-404. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.02.004. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22425180 Review.
-
Monoallelic Gene Expression in Mammals.Annu Rev Genet. 2016 Nov 23;50:317-327. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120215-035120. Annu Rev Genet. 2016. PMID: 27893959 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding sex differences in human immunity through systems immunology.Oxf Open Immunol. 2025 Jul 4;6(1):iqaf006. doi: 10.1093/oxfimm/iqaf006. eCollection 2025. Oxf Open Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40692743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Clonal Analysis Reveals Random Monoallelic Expression in Lymphocytes That Traces Back to Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 8;10:827774. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.827774. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36003148 Free PMC article.
-
X-chromosome-linked miR-542-5p as a key regulator of sex disparity in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis by promoting Th17 differentiation.Biomark Res. 2025 Mar 1;13(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00741-x. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 40025567 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF-mediated insulation and chromatin environment modulate Car5b escape from X inactivation.BMC Biol. 2025 Mar 3;23(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02137-7. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40025499 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

