Plant Extracts in Obesity: A Role of Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 34631766
- PMCID: PMC8495072
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.727951
Plant Extracts in Obesity: A Role of Gut Microbiota
Abstract
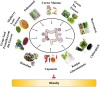
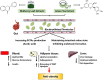
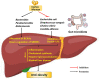
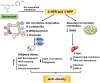
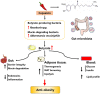
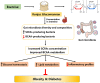
Obesity has become one of the most serious chronic diseases threatening human health. Its occurrence and development are closely associated with gut microbiota since the disorders of gut microbiota can promote endotoxin production and induce inflammatory response. Recently, numerous plant extracts have been proven to mitigate lipid dysmetabolism and obesity syndrome by regulating the abundance and composition of gut microbiota. In this review, we summarize the potential roles of different plant extracts including mulberry leaf extract, policosanol, cortex moutan, green tea, honokiol, and capsaicin in regulating obesity via gut microbiota. Based on the current findings, plant extracts may be promising agents for the prevention and treatment of obesity and its related metabolic diseases, and the mechanisms might be associated with gut microbiota.
Keywords: gut microbiota; lipid metabolism; mechanisms; obesity; plant extracts.
Copyright © 2021 Weng, Duan, Zhong, Song, Zheng, Zhang, Yin and Deng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mulberry leaf phenolics and fiber exert anti-obesity through the gut microbiota-host metabolism pathway.J Food Sci. 2021 Apr;86(4):1432-1447. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15679. Epub 2021 Mar 24. J Food Sci. 2021. PMID: 33761137
-
Fubrick tea attenuates high-fat diet induced fat deposition and metabolic disorder by regulating gut microbiota and caffeine metabolism.Food Funct. 2020 Aug 1;11(8):6971-6986. doi: 10.1039/d0fo01282c. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32697259
-
Green Tea and Its Relation to Human Gut Microbiome.Molecules. 2021 Jun 26;26(13):3907. doi: 10.3390/molecules26133907. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34206736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The metabolic and vascular protective effects of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf extract in diet-induced obesity in mice are related to the amelioration of gut microbiota dysbiosis and to its immunomodulatory properties.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Dec;150:104487. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104487. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31610229
-
Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits.Br J Nutr. 2010 Aug;104 Suppl 2:S1-63. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510003363. Br J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20920376 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Triphala extracts on the changes of obese fecal microbiome and metabolome in the human gut model.J Tradit Complement Med. 2023 Feb 28;13(2):207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.02.011. eCollection 2023 Mar. J Tradit Complement Med. 2023. PMID: 36970454 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tea Seed Oil Extracted by Different Refining Temperatures on the Intestinal Microbiota of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Foods. 2024 Jul 26;13(15):2352. doi: 10.3390/foods13152352. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123544 Free PMC article.
-
Brevibacillus laterosporus BL1, a promising probiotic, prevents obesity and modulates gut microbiota in mice fed a high-fat diet.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 24;9:1050025. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1050025. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36505236 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin: Emerging Pharmacological and Therapeutic Insights.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jul 24;46(8):7895-7943. doi: 10.3390/cimb46080468. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39194685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Interaction between Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Gut Microbiota in the Antioxidant Effects of Extracts from Sonchus brachyotus DC. in Oxazolone-Induced Intestinal Oxidative Stress in Adult Zebrafish.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;12(1):192. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010192. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671053 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

