Origanum majorana L.: A Nutritional Supplement With Immunomodulatory Effects
- PMID: 34631774
- PMCID: PMC8493290
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2021.748031
Origanum majorana L.: A Nutritional Supplement With Immunomodulatory Effects
Abstract
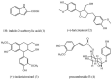
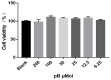
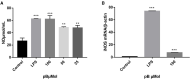
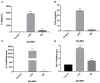
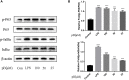
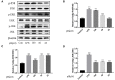
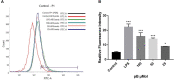
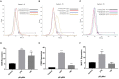
Origanum majorana L. is an aromatic herb that has been grown in several Mediterranean countries since ancient times, but became popular during the Middle Ages as a medicinal plant and seasoning ingredient. O. majorana has many pharmacological effects, but its immunoreactive components and mechanisms are still unclear. In this study, four compounds were isolated and identified from O. majorana by a spectral analysis, including 1H and 13C-NMR. They were 1H-indole-2-carboxylic acid (1), (+)-laricresol (2), (+)-isolaricresol (3), and procumboside B (4, pB), which were isolated for the first time in O. majorana. The immunomodulatory effects of the four compounds were screened, and pB had good immunomodulatory activity on RAW 264.7 cells. The immunomodulatory mechanism of pB was proved, in which pB could increase the secretion of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) and simultaneously upregulate the expression of CD80 and CD86 on the cell surface. These results suggested that the mechanism of pB may be related to the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)-signaling pathways. O. majorana is rich in nutrients and is commonly used in diets, so it can be used as a nutritional supplement with immunomodulatory effects.
Keywords: MAPKs; NF-κB; Origanum majorana L.; RAW264.7; immune; procumboside B.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Zhou, Attia, Tang, Wang, Liu, Waterhouse, Liu and Kang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Traditional use, phytochemistry, toxicology, and pharmacology of Origanum majorana L.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 30;265:113318. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113318. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32882360 Review.
-
A polysaccharide isolated from the fruits of Physalis alkekengi L. induces RAW264.7 macrophages activation via TLR2 and TLR4-mediated MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Nov 1;140:895-906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.174. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31442508
-
Potential Mechanisms of Imidacloprid-Induced Neurotoxicity in Adult Rats with Attempts on Protection Using Origanum majorana L. Oil/Extract: In Vivo and In Silico Studies.ACS Omega. 2023 May 17;8(21):18491-18508. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c08295. eCollection 2023 May 30. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37273614 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of total flavonoids of Astragalus by regulating NF-ΚB and MAPK signalling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Pharmazie. 2018 Oct 1;73(10):589-593. doi: 10.1691/ph.2018.8633. Pharmazie. 2018. PMID: 30223923
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of Aureusidin in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via suppressing NF-κB and activating ROS- and MAPKs-dependent Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 15;387:114846. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114846. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31790703
Cited by
-
The Immunomodulatory Effects of Active Ingredients From Nigella sativa in RAW264.7 Cells Through NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathways.Front Nutr. 2022 May 31;9:899797. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.899797. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35711536 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial, Multidrug Resistance Reversal and Biofilm Formation Inhibitory Effect of Origanum majorana Extracts, Essential Oil and Monoterpenes.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 27;11(11):1432. doi: 10.3390/plants11111432. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mona F. Bioactivities and biochemical effects of marjoram essential oil used against potato tuber mothphthorimaeaoperculella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). Life Sci J. (2011) 8:288–98. 10.7537/marslsj080111.35 - DOI
-
- Jiang Z, Li R, Wang Y, Chen S, Guan W. Volatile oil composition of natural spice, Origanum majorana L. grown in China. J Essential Oil Bearing Plants. (2011) 4:458–62. 10.1080/0972060X.2011.10643601 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

