Comprehensive Analysis of m5C RNA Methylation Regulator Genes in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 34631874
- PMCID: PMC8497170
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3803724
Comprehensive Analysis of m5C RNA Methylation Regulator Genes in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Recent research found that N5-methylcytosine (m5C) was involved in the development and occurrence of numerous cancers. However, the function and mechanism of m5C RNA methylation regulators in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) remains undiscovered. This study is aimed at investigating the predictive and clinical value of these m5C-related genes in ccRCC.
Methods: Based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database, the expression patterns of twelve m5C regulators and matched clinicopathological characteristics were downloaded and analyzed. To reveal the relationships between the expression levels of m5C-related genes and the prognosis value in ccRCC, consensus clustering analysis was carried out. By univariate Cox analysis and last absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) Cox regression algorithm, a m5C-related risk signature was constructed in the training group and further validated in the testing group and the entire cohort. Then, the predictive ability of survival of this m5C-related risk signature was analyzed by Cox regression analysis and nomogram. Functional annotation and single-sample Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (ssGSEA) were applied to further explore the biological function and potential signaling pathways. Furthermore, we performed qRT-PCR experiments and measured global m5C RNA methylation level to validate this signature in vitro and tissue samples.
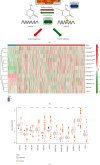
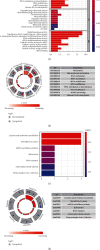
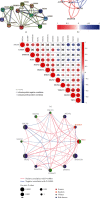
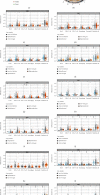
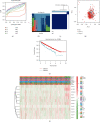
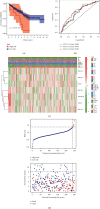
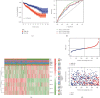
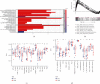
Results: In the TCGA-KIRC cohort, we found significant differences in the expression of m5C RNA methylation-related genes between ccRCC tissues and normal kidney tissues. Consensus cluster analysis was conducted to separate patients into two m5C RNA methylation subtypes. Significantly better outcomes were observed in ccRCC patients in cluster 1 than in cluster 2. m5C RNA methylation-related risk score was calculated to evaluate the prognosis of ccRCC patients by seven screened m5C RNA methylation regulators (NOP2, NSUN2, NSUN3, NSUN4, NSUN5, TET2, and DNMT3B) in the training cohort. The AUC for the 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival in the training cohort were 0.792, 0.675, and 0.709, respectively, indicating that the risk signature had an excellent prognosis prediction in ccRCC. Additionally, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses revealed that the risk signature could be an independent prognostic factor in ccRCC. The results of ssGSEA suggested that the immune cells with different infiltration degrees between the high-risk and low-risk groups were T cells including follicular helper T cells, Th1_cells, Th2_cells, and CD8+_T_cells, and the main differences in immune-related functions between the two groups were the interferon response and T cell costimulation. In addition, qRT-PCR experiments confirmed our results in renal cell lines and tissue samples.
Conclusions: According to the seven selected regulatory factors of m5C RNA methylation, a risk signature associated with m5C methylation that can independently predict prognosis in patients with ccRCC was developed and further verified the predictive efficiency.
Copyright © 2021 Jiajin Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic Value of an m5C RNA Methylation Regulator-Related Signature for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Aug 24;13:6673-6687. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S323072. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 34471382 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of overall survival based upon a new ferroptosis-related gene signature in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Apr 14;20(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02555-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35422048 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Methylation-Regulating Genes Prognostic Signature to Predict the Prognosis and Aid Immunotherapy of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 2;10:832803. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.832803. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35309925 Free PMC article.
-
A new CCCH-type zinc finger-related lncRNA signature predicts the prognosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 30;13:1034567. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1034567. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246657 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Prognostic Expression Markers for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 28;11:643065. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.643065. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NSUN4 Facilitates the Activity of Oncogenic Protein CDC20 to Promote NSCLC Development by Mediating m5C Modification of CDC20 mRNA.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Mar;16(5):e70023. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70023. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40051202 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics identify ribosome related causal genes methylation, splicing, and expression in prostate cancer.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 12;16(1):740. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02584-2. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40354008 Free PMC article.
-
Knocking down NSUN5 inhibits the development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting the p53 pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jun 1;15(11):4757-4773. doi: 10.18632/aging.204761. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37263638 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of RNA modification regulators index predicting clinical outcomes and immune relevance of kidney cancer patients.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 5;10(20):e39021. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39021. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39640638 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of m5C RNA Modification-Related Genes to Prognosis and Immunotherapy Prediction in Patients with Ovarian Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Nov 13;2023:1400267. doi: 10.1155/2023/1400267. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 38022687 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

