Reliability of Preoperative Planning Method That Considers Latent Medial Joint Laxity in Medial Open-Wedge Proximal Tibial Osteotomy
- PMID: 34631902
- PMCID: PMC8495530
- DOI: 10.1177/23259671211034151
Reliability of Preoperative Planning Method That Considers Latent Medial Joint Laxity in Medial Open-Wedge Proximal Tibial Osteotomy
Abstract
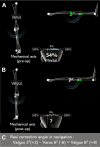
Background: Soft tissue laxity around the knee joint has been recognized as a crucial factor affecting correction error during medial open-wedge proximal tibial osteotomy (MOWPTO). Medial laxity in particular, which represents the changes in joint-line convergence angle (JLCA), affects soft tissue correction.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to quantify medial laxity and develop a preoperative planning method that considers medial laxity.
Study design: Cohort study; Level of evidence, 3.
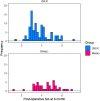
Methods: This study retrospectively reviewed 139 knees in 117 patients who underwent navigation-assisted MOWPTO from January 2014 to July 2019 for symptomatic medial compartment osteoarthritis with varus alignment >5°. We compared the results of 2 preoperative planning methods: conventional Miniaci (n = 47) and latent medial laxity reduction (LMLR) (n = 92). We evaluated the incidence of undercorrection, acceptable correction, and overcorrection. The radiologic parameters were analyzed using multiple linear regression with a stepwise selection model to establish an equation for the optimal preoperative planning method. The intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) of intraobserver, interobserver, and intermethod reliability were calculated.
Results: The Miniaci method showed a higher incidence of overcorrection (55.3%) than the LMLR method (22.8%) at postoperative 6 months (P = .0006). Multiple linear regression with a stepwise selection model revealed a high correlation coefficient (R 2 = 0.888) for the following equation: Adjusted planned correction angle = 0.596 + 0.891 × Target correction angle - 0.255 × ΔJLCA valgus . Upon simplification, the following equation showed the highest intermethod ICC value (0.991): Target correction angle - ⅓ΔJLCA valgus , while the Miniaci method showed a relatively low ICC value of 0.875.
Conclusion: There was a risk of overcorrection after MOWPTO using the conventional Miniaci method. An equation that considers medial laxity may help during preoperative planning for optimal correction during MOWPTO.
Keywords: correction error; medial laxity; preoperative planning; proximal tibial osteotomy.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
One or more of the authors has declared the following potential conflict of interest or source of funding: This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1A2B3007362 and 2015R1A2A1A15054779 to J.H.W.). AOSSM checks author disclosures against the Open Payments Database (OPD). AOSSM has not conducted an independent investigation on the OPD and disclaims any liability or responsibility relating thereto.
Figures



References
-
- Akamatsu Y, Mitsugi N, Mochida Y, et al. Navigated opening wedge high tibial osteotomy improves intraoperative correction angle compared with conventional method. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(3):586–593. doi:10.1007/s00167-011-1616-8 - PubMed
-
- Bito H, Takeuchi R, Kumagai K, et al. A predictive factor for acquiring an ideal lower limb realignment after opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(4):382–389. doi:10.1007/s00167-008-0706-8 - PubMed
-
- Brouwer RW, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, van Raaij TM, Verhaar JAN. Osteotomy for medial compartment arthritis of the knee using a closing wedge or an opening wedge controlled by a Puddu plate: a one-year randomised, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(11):1454–1459. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.88B11.17743 - PubMed
-
- Dowd GSE, Somayaji HS, Uthukuri M. High tibial osteotomy for medial compartment osteoarthritis. Knee. 2006;13(2):87–92. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2005.08.002 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

