Drug resistance mutations in protease gene of HIV-1 subtype C infected patient population
- PMID: 34631975
- PMCID: PMC8473514
- DOI: 10.1007/s13337-021-00725-z
Drug resistance mutations in protease gene of HIV-1 subtype C infected patient population
Abstract
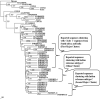
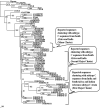
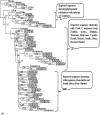
Failure of antiretroviral therapy (ART) in HIV-1 infection is a critical issue for the physicians treating HIV patients. The major cause of drug failure is the development of resistance mutations in reverse transcriptase (RT) and/or protease (PR) genes. Mutations associated with drug resistance decrease drug effectiveness. This study was conducted to assess drug resistance profile of the entire PR gene in 90 HIV-1 patients consisting of 23 ART non-responsive, 32 ART responsive and 35 drug naive patients. It was observed that the majority of the sequences (94.4%) belonged to subtype C and (5.5%) to subtype A1. The ART non-responsive and responsive patients were treated with either first line of ART regimen (two NRTI and one NNRTI) or second line of ART regimen that included additional one protease inhibitor (PI). All the patients in each group except one responsive patient had various minor resistance mutations. Thus, drug failures in ART non-responsive patients may not always be due to drug resistance mutations instead other factors may also be responsible for drug failures such as non-compliance, suboptimal dose or drug interaction. The presence of minor drug resistance mutations in drug naive patients is suggestive of transmitted resistance mutations.
Keywords: ART; Drug naive patients; Drug resistance; HIV-1; Protease gene; Protease inhibitors.
© Indian Virological Society 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 drug resistance genotyping from antiretroviral therapy (ART) naïve and first-line treatment failures in Djiboutian patients.Diagn Pathol. 2012 Oct 8;7:138. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-138. Diagn Pathol. 2012. PMID: 23044036 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of drug resistance mutations in the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase gene in patients who are non-responsive, responsive and naive to antiretroviral therapy.Arch Virol. 2016 May;161(5):1101-13. doi: 10.1007/s00705-016-2760-8. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Arch Virol. 2016. PMID: 26801790
-
Mutations in the reverse transcriptase and protease genes of human immunodeficiency virus-1 from antiretroviral naïve and treated pediatric patients.Viruses. 2015 Feb 10;7(2):590-603. doi: 10.3390/v7020590. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 25674767 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the impact of HIV genotypic drug resistance testing on therapy efficacy.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001;63(5):447-73. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001. PMID: 11813503 Review.
-
Lopinavir/ritonavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection.Drugs. 2003;63(8):769-802. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00004. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662125 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Computational Approaches for Understanding Drug Resistance in HIV-1 Protease Subtype C.Viruses. 2025 Jun 16;17(6):850. doi: 10.3390/v17060850. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40573441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of HIV Drug Resistance Mutations among Treatment-Naive People Living with HIV in a Tertiary Care Center in India.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024 Mar 5;110(4):713-718. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0026. Print 2024 Apr 3. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024. PMID: 38442417 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

