R-2HG downregulates ERα to inhibit cholangiocarcinoma via the FTO/m6A-methylated ERα/miR16-5p/YAP1 signal pathway
- PMID: 34632051
- PMCID: PMC8479483
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.06.017
R-2HG downregulates ERα to inhibit cholangiocarcinoma via the FTO/m6A-methylated ERα/miR16-5p/YAP1 signal pathway
Abstract
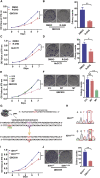
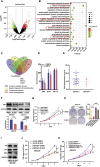
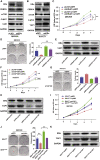
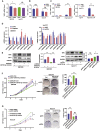
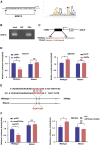
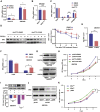
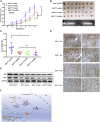
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutations increase (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate (R-2HG) production; however, functional mechanisms of R-2HG in regulating cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) development remain to be further investigated. We first applied the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing system to create IDH1R132H-mutated CCA cells. Interestingly, our data showed that R-2HG could function through downregulating estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) pathways to decrease CCA growth. Detailed mechanistic studies revealed that R-2HG could target and degrade the fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO), the first identified mRNA demethylase. This reduced FTO can increase the N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) to methylate the mRNA of ERα, and consequently decrease protein translation of the ERα. Further mechanistic studies revealed that ERα could transcriptionally suppress miR-16-5p expression, which could then increase YAP1 expression due to the reduced miR-16-5p binding to the 3' UTR of YAP1. Furthermore, data from the pre-clinical animal model with implantation of IDH1R132H QBC939 cells demonstrated that R-2HG generated by the IDH1 mutation could downregulate ERα and YAP1 to suppress CCA tumor growth. Taken together, our new findings suggested that IDH1 mutation-induced R-2HG could suppress CCA growth via regulating the FTO/m6A-methylated ERα/miR16-5p/YAP1 signaling pathway. Upregulating R-2HG or downregulating the ERα signal by short hairpin RNA ERα (shERα) or antiestrogen could be effective strategies to inhibit CCA.
Keywords: (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate; ERα; YAP1; cholangiocarcinoma; miR16-5p.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
R-2HG Exhibits Anti-tumor Activity by Targeting FTO/m6A/MYC/CEBPA Signaling.Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):90-105.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.031. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29249359 Free PMC article.
-
R-2-hydroxyglutarate attenuates aerobic glycolysis in leukemia by targeting the FTO/m6A/PFKP/LDHB axis.Mol Cell. 2021 Mar 4;81(5):922-939.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.12.026. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33434505 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating oncometabolite D-2-hydroxyglutarate enantiomer is a surrogate marker of isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutated intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas.Eur J Cancer. 2018 Feb;90:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.11.024. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29274619
-
Long Non-coding RNA MIR4435-2HG Promotes Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Metastasis Through miR-206/YAP1 Axis.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 20;10:160. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00160. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32154166 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant IDH1 Depletion Downregulates Integrins and Impairs Chondrosarcoma Growth.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 6;12(1):141. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010141. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31935911 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
METTL3-dependent m6A methylation facilitates uterine receptivity and female fertility via balancing estrogen and progesterone signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Jun 3;14(6):349. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05866-1. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37270544 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK3 deficiency blocks R-2-hydroxyglutarate-induced necroptosis in IDH-mutated AML cells.Sci Adv. 2024 Apr 19;10(16):eadi1782. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi1782. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38630819 Free PMC article.
-
The role of N(6)-methyladenosine (m6a) modification in cancer: recent advances and future directions.EXCLI J. 2025 Jan 15;24:113-150. doi: 10.17179/excli2024-7935. eCollection 2025. EXCLI J. 2025. PMID: 39967906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on the role of mir-16-5p in the carcinogenesis.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Nov 8;22(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02754-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36348403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M6A RNA methylation in biliary tract cancer: the function roles and potential therapeutic implications.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Feb 16;10(1):83. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01849-z. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38365891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khan S.A., Thomas H.C., Davidson B.R., Taylor-Robinson S.D. Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 2005;366:1303–1314. - PubMed
-
- Watanapa P. Cholangiocarcinoma in patients with opisthorchiasis. Br. J. Surg. 1996;83:1062–1064. - PubMed
-
- Dreyer C., Le Tourneau C., Faivre S., Qian Z., Degos F., Vuillerme M.P., Paradis V., Hammel P., Ruszniewski P., Cortes A. [Cholangiocarcinoma: epidemiology and global management] Rev. Med. Interne. 2008;29:642–651. - PubMed
-
- El-Diwany R., Pawlik T.M., Ejaz A. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2019;28:587–599. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

