Age-related differences in hypoxia-associated genes and cytokine profile in male Wistar rats
- PMID: 34632150
- PMCID: PMC8488852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08085
Age-related differences in hypoxia-associated genes and cytokine profile in male Wistar rats
Abstract
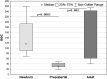
Hypoxia tolerance of the organism depends on many factors, including age. High newborn organisms tolerance and high level of oxidative stress throughout aging were demonstrated by many studies. However, there is lack of investigations reflecting the expression of key hypoxia-inducible factor HIF in different age organisms in correlation to levels of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Liver is a sensitive to hypoxia organ, and is an important organ in providing an acute reaction to infections - it synthesizes acute inflammation phase proteins, in particular, C-reactive protein. The aim of study was to determine relationship between age-related tolerance to hypoxia and HIF-1 and PHD2 (prolyl hydroxylase domain protein) expression levels in the liver and the production of cytokines in the spleen in newborn, prepubertal and adult Wistar rats. Newborn rats are characterized by high mRNA Hif-1α expression level in the liver, accompanied by a low content of HIF-1 protein and high level of PHD2. The growth in HIF-1α protein level throughout age is accompanied by the growth of pro-inflammatory cytokines level. Prepubertal animals are the least hypoxia resistant and their HIF-1α mRNA expression level was higher than in adult animals. The PHD2 activity in prepubertal animals was significantly reduced in comparison to newborn rats, and the HIF-1α protein level did not change. Further studies require the identification of additional mechanisms, determining the regulation of the HIF-1α level in prepubertal animals.
Keywords: Age-related differences; HIF-1; Hypoxia tolerance; Newborn; PHD2; Prepubertal age.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Reciprocal regulation between hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and its prolyl hydroxylases in hypoxic pulmonary hypertension rats].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2006 Oct;29(10):668-73. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17129494 Chinese.
-
miR-21 contributes to renal protection by targeting prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2 in delayed ischaemic preconditioning.Nephrology (Carlton). 2017 May;22(5):366-373. doi: 10.1111/nep.12787. Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. PMID: 27030384
-
Molecular characterization and mRNA expression of HIF-prolyl hydroxylase-2 (phd2) in hypoxia-sensing pathways from Megalobrama amblycephala.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Aug;186:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25868626
-
Transforming growth factor beta1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1 stabilization through selective inhibition of PHD2 expression.J Biol Chem. 2006 Aug 25;281(34):24171-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604507200. Epub 2006 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16815840
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) promotes its degradation by induction of HIF-alpha-prolyl-4-hydroxylases.Biochem J. 2004 Aug 1;381(Pt 3):761-7. doi: 10.1042/BJ20040620. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15104534 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Morphofunctional Changes in Brain and Peripheral Blood in Adult and Aged Wistar Rats with AlCl3-Induced Neurodegeneration.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 22;11(9):2336. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092336. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson J.L., Hooper W.C., Jones D.P., Ashfaq S., Rhodes S.D., Weintraub W.S., Harrison D.G., Quyyumi A.A., Vaccarino V. Association between novel oxidative stress markers and C-reactive protein among adults without clinical coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis. 2005;178:115–121. - PubMed
-
- Adolph E.F. Regulations during survival without oxygen in infant mammals. Respir. Physiol. 1969;7:356–368. - PubMed
-
- Appelhoff R.J., Tian Y.M., Raval R.R., Turley H., Harris A.L., Pugh C.W., Ratcliffe P.J., Gleadle J.M. Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3 in the regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:38458–38465. - PubMed
-
- Belaiba R.S., Bonello S., Zähringer C., Schmidt S., Hess J., Kietzmann T., Görlach A. Hypoxia up-regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha transcription by involving phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and nuclear factor kappaB in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2007;18:4691–4697. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

