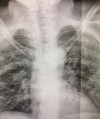
[GLUT1 and COVID-19 deficiency syndrome]
- PMID: 34632289
- PMCID: PMC7462458
- DOI: 10.1016/j.endinu.2020.07.001
[GLUT1 and COVID-19 deficiency syndrome]
Figures
References
-
- Leen W.G., Taher M., Verbeek M.M., Kamsteeg E.J., Van de Warrenburg B.P., Willemsen M.A. GLUT1 deficiency syndrome into adulthood: a follow-up study. J Neurol. 2014;261(3):589–599. doi:10.1007/s00415-014-7240-z. - PubMed
-
- Pasca L., De Giorgis V., Macasaet J.A., Trentani C., Tagliabue A., Veggiotti P. The changing face of dietary therapy for epilepsy. Eur J Pediatr. 2016;175(10):1267–1276. doi:10.1007/s00431-016-2765-z. - PubMed
-
- Kim J.A., Yoon J.R., Lee E.J., Lee J.S., Kim J.T., Kim H.D., et al. Efficacy of the classic ketogenic and the modified Atkins diets in refractory childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2016;57(1):51–58. doi:10.1111/epi.13256. - PubMed
-
- Zavala M., Castillo V., González M., Castillo S. Síndrome de deficiencia de GLUT-1 [GLUT-1 deficiency syndrome] Rev Neurol. 2019;69(4):178–179. doi:10.33588/rn.6904.2019126. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous