Consensus Virtual Screening Identified [1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-b]isoquinolines As MELK Inhibitor Chemotypes
- PMID: 34632716
- PMCID: PMC9298037
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202100569
Consensus Virtual Screening Identified [1,2,4]Triazolo[1,5-b]isoquinolines As MELK Inhibitor Chemotypes
Abstract
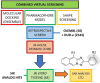
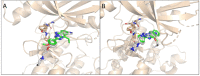
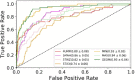
Maternal Embryonic Leucine-zipper Kinase (MELK) is a current oncotarget involved in a diverse range of human cancers, with the usage of MELK inhibitors being explored clinically. Here, we aimed to discover new MELK inhibitor chemotypes from our in-house compound library with a consensus-based virtual screening workflow, employing three screening concepts. After careful retrospective validation, prospective screening and in vitro enzyme inhibition testing revealed a series of [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-b]isoquinolines as a new structural class of MELK inhibitors, with the lead compound of the series exhibiting a sub-micromolar inhibitory activity. The structure-activity relationship of the series was explored by testing further analogs based on a structure-guided selection process. Importantly, the present work marks the first disclosure of the synthesis and bioactivity of this class of compounds.
Keywords: MELK inhibitor; docking; isoquinoline; kinase; virtual screening.
© 2021 The Authors. ChemMedChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel inhibitor discovery through virtual screening against multiple protein conformations generated via ligand-directed modeling: a maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase example.J Chem Inf Model. 2012 May 25;52(5):1345-55. doi: 10.1021/ci300040c. Epub 2012 May 8. J Chem Inf Model. 2012. PMID: 22540736
-
Phytochemical-Based Drug Discovery for Breast Cancer: Combining Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics to Identify Novel Therapeutics.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Jun;22(6):e202402864. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202402864. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39868843
-
Discovery of a potent inhibitor of MELK that inhibits expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1 and TNBC cell growth.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 May 1;25(9):2609-2616. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.03.018. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28351607
-
Targeting MELK in tumor cells and tumor microenvironment: from function and mechanism to therapeutic application.Clin Transl Oncol. 2025 Mar;27(3):887-900. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03664-5. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Clin Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39187643 Review.
-
MELK: a potential novel therapeutic target for TNBC and other aggressive malignancies.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Sep;21(9):849-859. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1363183. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28764577 Review.
References
-
- Heyer B. S., Warsowe J., Solter D., Knowles B. B., Ackerman S. L., Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1997, 47, 148–156. - PubMed
-
- Jiang P., Zhang D., Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, Vol. 14, Pages 21551–21560 2013, 14, 21551–21560.
-
- Gray D., Jubb A. M., Hogue D., Dowd P., Kljavin N., Yi S., Bai W., Frantz G., Zhang Z., Koeppen H., de Sauvage F. J., Davis D. P., Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9751–9761. - PubMed
-
- Choi S., Ku J. L., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 207–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

