Novel angular naphthopyrone formation by Arp1p dehydratase involved in Aspergillus fumigatus melanin biosynthesis
- PMID: 34632721
- PMCID: PMC8612989
- DOI: 10.1111/1758-2229.13013
Novel angular naphthopyrone formation by Arp1p dehydratase involved in Aspergillus fumigatus melanin biosynthesis
Abstract
Conidial pigment is an important virulence factor in Aspergillus fumigatus, a human fungal pathogen. The biosynthetic gene cluster for 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene (DHN)-melanin in A. fumigatus consists of six genes, alb1, ayg1, arp1, arp2, abr1 and abr2. In contrast to black DHN-melanin fungi such as Magnaporthe grisea, the polyketide synthase Alb1p in A. fumigatus produces naphthopyrone YWA1 instead of 1,3,6,8-THN (T4HN) and YWA1 is converted to T4HN by Ayg1p. The yeast transformant expressing Alb1p and Arp1p dehydratase produced an unknown compound which was identified to be a novel angular naphthopyrone named YWA3 formed from YWA1. In addition, the amount of YWA3 produced was much more than that of YWA2 formed by non-enzymatic dehydration from YWA1. To further analyse the reaction in vitro, Arp1p was overexpressed in E. coli and purified. Kinetic analysis revealed Km value of Arp1p for YWA1 to be 41 μM which is comparable with that of Ayg1p for YWA1 in conversion to T4HN. The complex structure modelling well explained the mechanism of YWA3 generation by the dehydration of angular YWA1 by Arp1p. These results indicated the possibility that polymerization of angular naphthopyrone YWA3 but not YWA2 could be involved in the characteristic bluish-green conidial pigmentation of A. fumigatus.
© 2021 Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest. None declared.
Figures


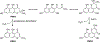


Similar articles
-
Hydrolytic polyketide shortening by ayg1p, a novel enzyme involved in fungal melanin biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 22;279(43):44613-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406758200. Epub 2004 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15310761
-
Aspergillus fumigatus alb1 encodes naphthopyrone synthase when expressed in Aspergillus oryzae.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000 Nov 1;192(1):39-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09356.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2000. PMID: 11040426
-
A developmentally regulated gene cluster involved in conidial pigment biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus.J Bacteriol. 1999 Oct;181(20):6469-77. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.20.6469-6477.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10515939 Free PMC article.
-
Melanin and pyomelanin in Aspergillus fumigatus: from its genetics to host interaction.Int Microbiol. 2020 Jan;23(1):55-63. doi: 10.1007/s10123-019-00078-0. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Int Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31020477 Review.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus conidial pigment and cAMP signal transduction: significance for virulence.Med Mycol. 2005 May;43 Suppl 1:S75-82. doi: 10.1080/13693780400028967. Med Mycol. 2005. PMID: 16110796 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing phenotype variants of Cercosporidium personatum, causal agent of peanut late leaf spot disease, their morphology, genetics and metabolites.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 9;15(1):1405. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85953-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39789282 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basarab GS, Steffens JJ, Wawrzak Z, Schwartz RS, Lundqvist T, and Jordan DB (1999) Catalytic mechanism of scytalone dehydratase: site-directed mutagenesis, kinetic isotope effects, and alternate substrates. Biochem 38: 6012–6024. - PubMed
-
- Fujii I, Yasuoka Y, Tsai H-F, Chang YC, Kwon-Chung KJ, and Ebizuka Y (2004) Hydrolytic polyketide shortening by Ayg1p, a novel enzyme involved in fungal melanin biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 279: 4613–44620. - PubMed
-
- Gietz RD, Schiestl RH, Willems AR, and Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 15: 355–360. - PubMed
-
- Gorst-Allman CP, Steyn PS, and Rabie CJ (1980) Structural elucidation of the nigerones, four new naphthopyrones from cultures of Aspergillus niger. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1 2474–2479.
-
- Hashida-Okada T, Ogawa A, Kato I, and Takesako K (1998) Transformation system for prototrophic industrial yeasts using the AUR1 gene as a dominant selection marker. FEBS Lett 425: 117–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

