A review: Antibody-dependent enhancement in COVID-19: The not so friendly side of antibodies
- PMID: 34632844
- PMCID: PMC8512237
- DOI: 10.1177/20587384211050199
A review: Antibody-dependent enhancement in COVID-19: The not so friendly side of antibodies
Abstract
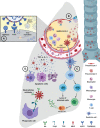
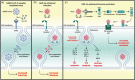
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), represents an unprecedented global public health emergency with economic and social consequences. One of the main concerns in the development of vaccines is the antibody-dependent enhancement phenomenon, better known as ADE. In this review, we provide an overview of SARS-CoV-2 infection as well as the immune response generated by the host. On the bases of this principle, we also describe what is known about the ADE phenomenon in various viral infections and its possible role as a limiting factor in the development of new vaccines and therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: ADE; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody-dependent enhancement; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Division of Viral Diseases (2020) Scientific Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Transmission. In CDC COVID-19 Science Briefs Atlanta (GA): Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US). - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Situation reports. [online] Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... (accessed April 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

