Influence of Modulation Factor on Treatment Plan Quality and Irradiation Time in Hippocampus-Sparing Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Using Tomotherapy
- PMID: 34632876
- PMCID: PMC8504207
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338211045497
Influence of Modulation Factor on Treatment Plan Quality and Irradiation Time in Hippocampus-Sparing Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Using Tomotherapy
Abstract
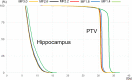
Objectives: Hippocampus-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy (HS-WBRT) using tomotherapy is known to provide a better dose distribution than volumetric-modulated arc therapy but requires an extended irradiation time. The present study aimed to investigate whether irradiation time can be shortened by reducing the modulation factor (MF) without losing the target dose distribution. Methods: Using six tilted computed tomography images in the head area, the planning target volume (PTV) and hippocampal doses, and the irradiation time was investigated with a jaw width of 1 cm, a pitch of 0.200, and the MF changed from 3.0 to 2.6, 2.2, 1.8, and 1.4. Results: No significant changes in the PTV or hippocampus were found with MF in the range from 3.0 to 1.8, but marked deterioration was found with that of 1.4. The irradiation time showed a linear relationship with the MF within the range from 3.0 to 1.8, with 1334, 1158, 986, and 817 s at modulation factors of 3.0, 2.6, 2.2, and 1.8, respectively. However, when the MF was 1.4, the irradiation time was 808 s. Conclusions: When HS-WBRT is performed with a tilted body position and a jaw width of 1 cm, with a MF of 1.8, a favorable balance between dose parameters and irradiation time is achieved, whereas with a MF of 1.4, the quality of the radiotherapy plan deteriorates, and the irradiation time is approximately the same as that with a MF of 1.8.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01780675 NCT02635009 NCT02397733.
Keywords: brain metastases; hippocampus-sparing; tilt heading; tomotherapy; whole-brain radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(34):3810-3816. doi:10.1200/JCO.2014.57.2909 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical