Dual-target inhibitors of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins in cancer: A review from medicinal chemistry perspectives
- PMID: 34633088
- PMCID: PMC8837683
- DOI: 10.1002/med.21859
Dual-target inhibitors of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins in cancer: A review from medicinal chemistry perspectives
Abstract
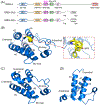
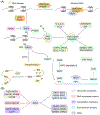
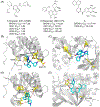
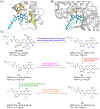
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4), as the most studied member of the bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) family, is a chromatin reader protein interpreting epigenetic codes through binding to acetylated histones and non-histone proteins, thereby regulating diverse cellular processes including cell cycle, cell differentiation, and cell proliferation. As a promising drug target, BRD4 function is closely related to cancer, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and liver fibrosis. Currently, clinical resistance to BET inhibitors has limited their applications but synergistic antitumor effects have been observed when used in combination with other tumor inhibitors targeting additional cellular components such as PLK1, HDAC, CDK, and PARP1. Therefore, designing dual-target inhibitors of BET bromodomains is a rational strategy in cancer treatment to increase potency and reduce drug resistance. This review summarizes the protein structures and biological functions of BRD4 and discusses recent advances of dual BET inhibitors from a medicinal chemistry perspective. We also discuss the current design and discovery strategies for dual BET inhibitors, providing insight into potential discovery of additional dual-target BET inhibitors.
Keywords: bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET); bromodomain-containing protein 4; dual-target inhibitors; medicinal chemistry; structure-activity relationship.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures






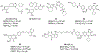
Similar articles
-
Selective inhibition of the BD2 bromodomain of BET proteins in prostate cancer.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7794):306-310. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1930-8. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31969702
-
BET Bromodomain as a Target of Epigenetic Therapy.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016;64(6):540-7. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c16-00225. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 27250788 Review.
-
A patent review of BRD4 inhibitors (2013-2019).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020 Jan;30(1):57-81. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1702645. Epub 2019 Dec 13. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020. PMID: 31815566 Review.
-
The Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Family: Functional Anatomy of BET Paralogous Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 7;17(11):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111849. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27827996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bromodomains: Structure, function and pharmacology of inhibition.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Apr 15;106:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.12.005. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26707800 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting SIRT1 synergistically improves the antitumor effect of JQ-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 9;9(11):e22093. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22093. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38045194 Free PMC article.
-
From PROTAC to inhibitor: Structure-guided discovery of potent and orally bioavailable BET inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 May 5;251:115246. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115246. Epub 2023 Mar 4. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36898329 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CBX3 with a Dual BET/PLK1 Inhibitor Enhances the Antitumor Efficacy of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Dec;10(36):e2302368. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302368. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37949681 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-204-5p Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Targeting BRD4 in a Rat Chronic Constrictive Injury Model.J Pain Res. 2022 Aug 18;15:2427-2435. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S371616. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36003288 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of programmed cell death by Brd4.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Dec 20;13(12):1059. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05505-1. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36539410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu SY, Chiang CM. The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor BRD4 and transcriptional regulation. j Biol Chem. 2007;282(18):13141–13145. - PubMed
-
- Arrowsmith CH, Bountra C, Fish PV, Lee K, Schapira M. Epigenetic protein families: a new frontier for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(5):384–400. - PubMed
-
- Romero FA, Taylor AM, Crawford TD, Tsui V, Côté A, Magnuson S. Disrupting acetyl-lysine recognition: progress in the development of bromodomain inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2016;59(4):1271–1298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

