IFN-γ mediates Paneth cell death via suppression of mTOR
- PMID: 34633285
- PMCID: PMC8570691
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60478
IFN-γ mediates Paneth cell death via suppression of mTOR
Abstract
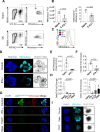
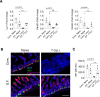
Paneth cells constitutively produce antimicrobial peptides and growth factors that allow for intestinal homeostasis, host protection, and intestinal stem cell replication. Paneth cells rely heavily on the glycolytic metabolic program, which is in part controlled by the kinase complex Mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTORC1). Yet, little is known about mTOR importance in Paneth cell integrity under steady-state and inflammatory conditions. Our results demonstrate that IFN-γ, a crucial mediator of the intestinal inflammation, acts directly on murine Paneth cells to alter their mitochondrial integrity and membrane potential, resulting in an TORC1-dependent cell death mechanism distinct from canonical cell death pathways including apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis. These results were established with the purified cytokine and a physiologically relevant common Th1-inducing human parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Given the crucial role for IFN-γ, which is a cytokine frequently associated with the development of inflammatory bowel disease and compromised Paneth cell functions, the identified mechanisms underlying mTORC1-dependent Paneth cell death downstream of IFN-γ may provide promising novel approaches for treating intestinal inflammation.
Keywords: IFN-gamma; Paneth cells; Toxoplasma; cell death; immunology; inflammation; intestine; mTOR; mouse.
© 2021, Araujo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AA, AS, EB, AL, SG, EC, AM, SG, FY No competing interests declared
Figures
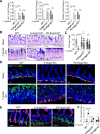
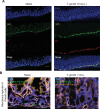
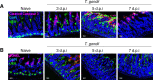
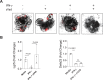

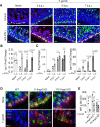

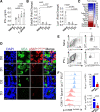
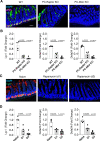
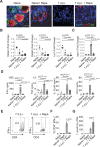
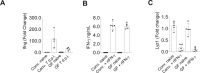

References
-
- Adolph TE, Tomczak MF, Niederreiter L, Ko HJ, Böck J, Martinez-Naves E, Glickman JN, Tschurtschenthaler M, Hartwig J, Hosomi S, Flak MB, Cusick JL, Kohno K, Iwawaki T, Billmann-Born S, Raine T, Bharti R, Lucius R, Kweon MN, Marciniak SJ, Choi A, Hagen SJ, Schreiber S, Rosenstiel P, Kaser A, Blumberg RS. Paneth cells as a site of origin for intestinal inflammation. Nature. 2013;503:272–276. doi: 10.1038/nature12599. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

