pH-responsive and folate-coated liposomes encapsulating irinotecan as an alternative to improve efficacy of colorectal cancer treatment
- PMID: 34634556
- PMCID: PMC9052206
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112317
pH-responsive and folate-coated liposomes encapsulating irinotecan as an alternative to improve efficacy of colorectal cancer treatment
Abstract
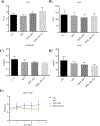
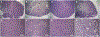
Irinotecan (IRN) is a semisynthetic derivative of camptothecin that acts as a topoisomerase I inhibitor. IRN is used worldwide for the treatment of several types of cancer, including colorectal cancer, however its use can lead to serious adverse effects, as diarrhea and myelosuppression. Liposomes are widely used as drug delivery systems that can improve chemotherapeutic activity and decrease side effects. Liposomes can also be pH-sensitive to release its content preferentially in acidic environments, like tumors, and be surface-functionalized for targeting purposes. Herein, we developed a folate-coated pH-sensitive liposome as a drug delivery system for IRN to reach improved tumor therapy without potential adverse events. Liposomes were prepared containing IRN and characterized for particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, concentration, encapsulation, cellular uptake, and release profile. Antitumor activity was investigated in a murine model of colorectal cancer, and its toxicity was evaluated by hematological/biochemical tests and histological analysis of main organs. The results showed vesicles smaller than 200 nm with little dispersion, a surface charge close to neutral, and high encapsulation rate of over 90%. The system demonstrated prolonged and sustained release in pH-dependent manner with high intracellular drug delivery capacity. Importantly, the folate-coated pH-sensitive formulation had significantly better antitumor activity than the pH-dependent system only or the free drug. Tumor tissue of IRN-containing groups presented large areas of necrosis. Furthermore, no evidence of systemic toxicity was found for the groups investigated. Thus, our developed nanodrug IRN delivery system can potentially be an alternative to conventional colorectal cancer treatment.
Keywords: Antitumor activity; Folate-coated; Irinotecan, polyethylene glycol; Liposomes.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

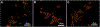
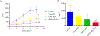

References
-
- Wei H, Song J, Li H, Li Y, Zhu S, Zhou X, Zhang X, Yang L, ScienceDirect Active loading liposomal irinotecan hydrochloride: preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation, Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 8 (2013) 303–311, 10.1016/j.ajps.2013.10.006. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

