Circadian effects of ionizing radiation on reproductive function and clock genes expression in male mouse
- PMID: 34635049
- PMCID: PMC8507176
- DOI: 10.1186/s12199-021-01021-4
Circadian effects of ionizing radiation on reproductive function and clock genes expression in male mouse
Abstract
Background: Exposure to the ionizing radiation (IR) encountered outside the magnetic field of the Earth poses a persistent threat to the reproductive functions of astronauts. The potential effects of space IR on the circadian rhythms of male reproductive functions have not been well characterized so far.
Methods: Here, we investigated the circadian effects of IR exposure (3 Gy X-rays) on reproductive functional markers in mouse testicular tissue and epididymis at regular intervals over a 24-h day. For each animal, epididymis was tested for sperm motility, and the testis tissue was used for daily sperm production (DSP), testosterone levels, and activities of testicular enzymes (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH), sorbitol dehydrogenase (SDH), lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), and acid phosphatase (ACP)), and the clock genes mRNA expression such as Clock, Bmal1, Ror-α, Ror-β, or Ror-γ.
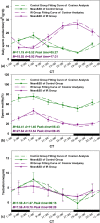
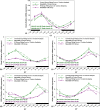
Results: Mice exposed to IR exhibited a disruption in circadian rhythms of reproductive markers, as indicated by decreased sperm motility, increased daily sperm production (DSP), and reduced activities of testis enzymes such as G6PDH, SDH, LDH, and ACP. Moreover, IR exposure also decreased mRNA expression of five clock genes (Clock, Bmal1, Ror-α, Ror-β, or Ror-γ) in testis, with alteration in the rhythm parameters.
Conclusion: These findings suggested potential health effects of IR exposure on reproductive functions of male astronauts, in terms of both the daily overall level as well as the circadian rhythmicity.
Keywords: Circadian rhythm; Clock genes; Ionizing radiation; Reproductive marker.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circadian alterations of reproductive functional markers in male rats exposed to 1800 MHz radiofrequency field.Chronobiol Int. 2014 Feb;31(1):123-33. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2013.830622. Epub 2013 Oct 11. Chronobiol Int. 2014. PMID: 24117058
-
RORγ directly regulates the circadian expression of clock genes and downstream targets in vivo.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Sep 1;40(17):8519-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks630. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22753030 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian rhythm genes mediate fenvalerate-induced inhibition of testosterone synthesis in mouse Leydig cells.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2017;80(23-24):1314-1320. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2017.1384148. Epub 2017 Oct 17. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2017. PMID: 29040059
-
Recent advances in the mechanisms of action and physiological functions of the retinoid-related orphan receptors (RORs).Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004 Dec;3(4):395-412. doi: 10.2174/1568010042634497. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15584888 Review.
-
[The roles of clock genes in obesity].Nihon Rinsho. 2013 Feb;71(2):244-8. Nihon Rinsho. 2013. PMID: 23631200 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Utility of melatonin in mitigating ionizing radiation-induced testis injury through synergistic interdependence of its biological properties.Biol Res. 2022 Nov 4;55(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00401-6. Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 36333811 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term space missions' effects on the human organism: what we do know and what requires further research.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 13;15:1284644. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1284644. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38415007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin Ameliorates 2.856 GHz Microwave- Radiation-Induced Reproductive Impairments in Male Rats via Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 31;24(15):12250. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512250. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569626 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal vitamin A supplementation improves sheep fertility potential.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 2;11:1370576. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1370576. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38756517 Free PMC article.
-
Copper-induced diurnal hepatic toxicity is associated with Cry2 and Per1 in mice.Environ Health Prev Med. 2023;28:78. doi: 10.1265/ehpm.23-00205. Environ Health Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 38092388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Squire T, Buchanan G, Elsaleh H. Mission to Mars: radiation safety or radiation disaster? Space transit and Mars radiation exposure risks-the shielding effect of a graphene space suit and a storm shelter during space travel. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2019;103:E44. doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(19)30509-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
