Modifiable risk factors for dementia and dementia risk profiling. A user manual for Brain Health Services-part 2 of 6
- PMID: 34635138
- PMCID: PMC8507172
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-021-00895-4
Modifiable risk factors for dementia and dementia risk profiling. A user manual for Brain Health Services-part 2 of 6
Abstract
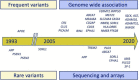
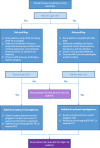
We envisage the development of new Brain Health Services to achieve primary and secondary dementia prevention. These services will complement existing memory clinics by targeting cognitively unimpaired individuals, where the focus is on risk profiling and personalized risk reduction interventions rather than diagnosing and treating late-stage disease. In this article, we review key potentially modifiable risk factors and genetic risk factors and discuss assessment of risk factors as well as additional fluid and imaging biomarkers that may enhance risk profiling. We then outline multidomain measures and risk profiling and provide practical guidelines for Brain Health Services, with consideration of outstanding uncertainties and challenges. Users of Brain Health Services should undergo risk profiling tailored to their age, level of risk, and availability of local resources. Initial risk assessment should incorporate a multidomain risk profiling measure. For users aged 39-64, we recommend the Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Aging, and Incidence of Dementia (CAIDE) Dementia Risk Score, whereas for users aged 65 and older, we recommend the Brief Dementia Screening Indicator (BDSI) and the Australian National University Alzheimer's Disease Risk Index (ANU-ADRI). The initial assessment should also include potentially modifiable risk factors including sociodemographic, lifestyle, and health factors. If resources allow, apolipoprotein E ɛ4 status testing and structural magnetic resonance imaging should be conducted. If this initial assessment indicates a low dementia risk, then low intensity interventions can be implemented. If the user has a high dementia risk, additional investigations should be considered if local resources allow. Common variant polygenic risk of late-onset AD can be tested in middle-aged or older adults. Rare variants should only be investigated in users with a family history of early-onset dementia in a first degree relative. Advanced imaging with 18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) or amyloid PET may be informative in high risk users to clarify the nature and burden of their underlying pathologies. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers are not recommended for this setting, and blood-based biomarkers need further validation before clinical use. As new technologies become available, advances in artificial intelligence are likely to improve our ability to combine diverse data to further enhance risk profiling. Ultimately, Brain Health Services have the potential to reduce the future burden of dementia through risk profiling, risk communication, personalized risk reduction, and cognitive enhancement interventions.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer’s disease; Brain health services; Dementia; Prevention; Public health; Risk factors; Risk profiling.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
GBF reports grants from Alzheimer Forum Suisse, Académie Suisse des Sciences Médicales, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, GE International, Guerbert, Association Suisse pour la Recherche sur l’Alzheimer, IXICO, Merz Pharma, Nestlé, Novartis, Piramal, Roche, Siemens, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Vifor Pharma, and Alzheimer’s Association; he has received personal fees from AstraZeneca, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Elan Pharmaceuticals, GE International, Lundbeck, Pfizer, and TauRx Therapeutics.
KB has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu. Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program.
JLM is currently a full time employee of Lundbeck and has previously served as a consultant or at advisory boards for the following for-profit companies, or has given lectures in symposia sponsored by the following for-profit companies: Roche Diagnostics, Genentech, Novartis, Lundbeck, Oryzon, Biogen, Lilly, Janssen, Green Valley, MSD, Eisai, Alector, BioCross, GE Healthcare, ProMIS Neurosciences.
All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Frisoni GB, Molinuevo JL, Altomare D, Carrera E, Barkhof F, Berkhof J, Delrieu J, Dubois B, Kivipelto M, Nordberg A, Schott JM, der Flier WM, Vellas B, Jessen F, Scheltens P, Ritchie C. Precision prevention of Alzheimer’s and other dementias: Anticipating future needs in the control of risk factors and implementation of disease-modifying therapies. Alzheimers Dement. 2020;16(10):1457–1468. doi: 10.1002/alz.12132. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altomare D, Molinuevo JL, Ritchie C, Ribaldi F, Carrera E, Dubois B, Jessen F, McWhirter L, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM, Vellas B, Démonet JF, Frisoni GB. Brain Health Services: Organization, structure and challenges for implementation. A user manual for Brain Health Services – Part 1 of 6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Visser LNC, Minguillon C, Sánchez-Benavides G, Abramowicz M, Altomare D, Fauria K, Frisoni GB, Georges J, Ribaldi F, Scheltens P, van der Schaar J, Zwan M, van der Flier WM, Molinuevo JL. Dementia risk communication. A user manual for Brain Health Services – Part 3 of 6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Solomon A, Stephen R, Altomare D, Carrera E, Frisoni GB, Kulmala J, Molinuevo JL, Nilsson P, Ngandu T, Ribaldi F, Vellas B, Scheltens P, Kivipelto M. Multidomain interventions: state-of-the-art and future directions for protocols to implement precision dementia risk reduction. A user manual for Brain Health Services – Part 4 of 6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brioschi Guevara A, Bieler M, Altomare D, Berthier M, Csajka C, Dautricourt S, Démonet JF, Dodich A, Frisoni GB, Miniussi C, Molinuevo JL, Ribaldi F, Scheltens P, Chételat G. Protocols for cognitive enhancement. A user manual for Brain Health Services – Part 5 of 6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

