Effects of Virtual Reality Training on Upper Limb Function and Balance in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34636735
- PMCID: PMC8548971
- DOI: 10.2196/31051
Effects of Virtual Reality Training on Upper Limb Function and Balance in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Virtual reality (VR) training is a promising intervention strategy that has been utilized in health care fields like stroke rehabilitation and psychotherapy. Current studies suggest that VR training is effective in improving the locomotor ability of stroke patients.
Objective: This is the first meta-meta-analysis of the effects of VR on motor function in stroke patients. This study aimed to systematically summarize and quantify the present meta-analyses results of VR training and produce high-quality meta-meta-analysis results to obtain a more accurate prediction.
Methods: We searched 4 online databases (Web of Science, Scopus, PubMed, and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure) for meta-analysis studies. After accounting for overlap, 10 studies (accounting for almost 550 stroke patients) were obtained. Based on the meta-meta-analysis of these patients, this study quantified the impact of VR training on stroke patients' motor performance, mainly including upper limb function, balance, and walking ability. We combined the effects under the random effect model and pooled the estimates as standardized mean differences (SMD).
Results: The results of the meta-meta-analysis showed that VR training effectively improves upper limb function (SMD 4.606, 95% CI 2.733-6.479, P<.05) and balance (SMD 2.101, 95% CI 0.202-4.000, P<.05) of stroke patients. However, the results showed considerable heterogeneity and thus, may need to be treated with caution. Due to the limited research, a meta-meta-analysis of walking ability was not performed.
Conclusions: These findings represent a comprehensive body of high-quality evidence that VR training is more effective at improving upper limb function and balance of stroke patients.
Keywords: digital intervention; health care; mental health; meta-meta-analysis; motor function; motor skills; rehabilitation; review; stroke; stroke patients; virtual reality.
©Jinlong Wu, Aihua Zeng, Ziyan Chen, Ye Wei, Kunlun Huang, Jiafeng Chen, Zhanbing Ren. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 12.10.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
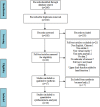


References
-
- Domínguez-Téllez P, Moral-Muñoz JA, Salazar A, Casado-Fernández E, Lucena-Antón D. Game-Based Virtual Reality Interventions to Improve Upper Limb Motor Function and Quality of Life After Stroke: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Games Health J. 2020 Feb 01;9(1):1–10. doi: 10.1089/g4h.2019.0043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Corbetta D, Imeri F, Gatti R. Rehabilitation that incorporates virtual reality is more effective than standard rehabilitation for improving walking speed, balance and mobility after stroke: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2015 Jul;61(3):117–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2015.05.017. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1836-9553(15)00056-9 S1836-9553(15)00056-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

