A case of hemobilia caused by pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma treated with a covered metallic stent
- PMID: 34637048
- PMCID: PMC8858272
- DOI: 10.1007/s12328-021-01532-1
A case of hemobilia caused by pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma treated with a covered metallic stent
Abstract
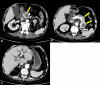
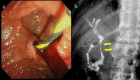
We present the case of an 86-year-old man who had undergone left nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma (clear cell carcinoma) 22 years ago. He visited the emergency department complaining of right hypochondrial pain and fever. He was eventually diagnosed with acute cholangitis. Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography showed multiple tumors in the pancreas. The tumor in the pancreatic head obstructed the distal bile duct. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography detected bloody bile juice flowing from the papilla of Vater. Therefore, he was diagnosed with hemobilia. Cholangiography showed extrinsic compression of the distal bile duct; a 6 Fr endoscopic nasobiliary drainage tube was placed. Endoscopic ultrasound showed that the pancreas contained multiple well-defined hypoechoic masses. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration was performed using a 22 G needle. Pathological examination revealed clear cell carcinoma, and the final diagnosis was pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) causing hemobilia. A partially covered metallic stent was placed in the distal bile duct. Consequently, hemobilia and cholangitis were resolved.
Keywords: Hemobilia; Metallic stent; Renal cell carcinoma.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Hemostasis with Metallic Stent for Multiple Metastatic Pancreatic Tumors Complicated with Hemobilia.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 6;18(1):58-67. doi: 10.1159/000536221. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38322757 Free PMC article.
-
Massive hemobilia following plastic stent removal in common bile duct cancer associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis (with video).Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb;12(1):46-51. doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0888-7. Epub 2018 Jul 28. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30056613
-
Etiology, clinical features, and endoscopic management of hemobilia: a retrospective analysis of 37 cases.Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012 Apr;59(4):296-302. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2012.59.4.296. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22544027
-
Hemobilia caused by pancreatic arteriovenous malformation: A case report and literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(50):e13285. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013285. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30557975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granular cell tumor of the pancreas diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018 Jun;11(3):193-199. doi: 10.1007/s12328-018-0821-0. Epub 2018 Jan 27. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29380119 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic hemostasis with a self-expandable metal stent as bridge therapy for hemobilia.Endosc Int Open. 2025 Jan 29;13:a24807065. doi: 10.1055/a-2480-7065. eCollection 2025. Endosc Int Open. 2025. PMID: 39958658 Free PMC article.
-
Hemostasis with Metallic Stent for Multiple Metastatic Pancreatic Tumors Complicated with Hemobilia.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 6;18(1):58-67. doi: 10.1159/000536221. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38322757 Free PMC article.
-
Isolated Pancreatic Metastases of Renal Cell Carcinoma-Clinical Particularities and Seed and Soil Hypothesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 4;15(2):339. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020339. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolated Pancreatic Metastases of Renal Cell Cancer: Genetics and Epigenetics of an Unusual Tumour Entity.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;14(6):1539. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061539. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma to Pancreas: Case Series and Review of the Literature.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;13(8):1368. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13081368. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37189469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

