Clinical Translation of Neutrophil Imaging and Its Role in Cancer
- PMID: 34637051
- PMCID: PMC8983506
- DOI: 10.1007/s11307-021-01649-2
Clinical Translation of Neutrophil Imaging and Its Role in Cancer
Abstract
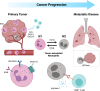
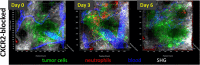
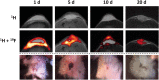
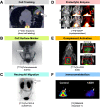
Neutrophils are the first line of defense against pathogens and abnormal cells. They regulate many biological processes such as infections and inflammation. Increasing evidence demonstrated a role for neutrophils in cancer, where different subpopulations have been found to possess both pro- or anti-tumorigenic functions in the tumor microenvironment. In this review, we discuss the phenotypic and functional diversity of neutrophils in cancer, their prognostic significance, and therapeutic relevance in human and preclinical models. Molecular imaging methods are increasingly used to probe neutrophil biology in vivo, as well as the cellular changes that occur during tumor progression and over the course of treatment. This review will discuss the role of neutrophil imaging in oncology and the lessons that can be drawn from imaging in infectious diseases and inflammatory disorders. The major factors to be considered when developing imaging techniques and biomarkers for neutrophils in cancer are reviewed. Finally, the potential clinical applications and the limitations of each method are discussed, as well as the challenges for future clinical translation.
Keywords: Cancer; Imaging; Immunotherapy; Infection; Inflammation; MRI; Neutrophils; Optical; PET; SPECT.
© 2021. Crown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mestas J, Hughes CCW. Of mice and not men: differences between mouse and human immunology. J Immunol. 2004;172:2731–2738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

