Nutritional interventions in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy: Current practice at the Dutch Head and Neck Oncology centres
- PMID: 34637563
- PMCID: PMC9285387
- DOI: 10.1111/ecc.13518
Nutritional interventions in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy: Current practice at the Dutch Head and Neck Oncology centres
Abstract
Objective: To assess variations in nutritional interventions during chemoradiotherapy (CRT) among the Dutch Head and Neck Oncology centres (HNOCs).
Methods: An online questionnaire about nutritional interventions and dietetic practices was sent to 14 oncology dietitians of the HNOCs.
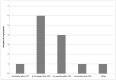
Results: The response rate was 93%. The number of scheduled dietetic consultations varied from two to seven during CRT. Most centres (77%) reported using a gastrostomy for tube feeding in the majority of patients. Gastrostomies were placed prophylactically upon indication (39%) or in all patients (15%), reactive (15%), or both (31%). For calculating energy requirements, 54% of the dietitians used the Food and Agriculture Organization/World Health Organization and United Nations University (FAO/WHO/UNU) formula and 77% uses 1.2-1.5 g/kg body weight for calculating protein requirements. Almost half of the centres (46%) reported to remove the gastrostomy between 8 and 12 weeks after CR. Most centres (92%) reported to end dietary treatment within 6 months after CRT.
Conclusion: This study shows substantial variation in dietetic practice, especially in the use of a gastrostomy for tube feeding, between the HNOCs. There is a need for concise dietetic guidelines.
Keywords: chemoradiotherapy; diet therapy; enteral nutrition; gastrostomy; head and neck neoplasms; nutritional intervention.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Cancer Care published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Beijer, S. D. P. , Doornink, N. , ten Have, H. , van Lieshout, R. , & Vogel, J. (2016). Voedingsbehoefte en voedingsadvies. In Vogel J. (Ed.), Handboek voeding bij kanker (second ed.) (pp. 64–80). De Tijdstroom.
-
- Berthiller, J. , Straif, K. , Agudo, A. , Ahrens, W. , Bezerra Dos Santos, A. , Boccia, S. , & Lee, Y. C. (2016). Low frequency of cigarette smoking and the risk of head and neck cancer in the INHANCE consortium pooled analysis. International Journal of Epidemiology, 45(3), 835–845. 10.1093/ije/dyv146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bressan, V. , Stevanin, S. , Bianchi, M. , Aleo, G. , Bagnasco, A. , & Sasso, L. (2016). The effects of swallowing disorders, dysgeusia, oral mucositis and xerostomia on nutritional status, oral intake and weight loss in head and neck cancer patients: A systematic review. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 45, 105–119. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.006 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials