Molecular Mechanism of EGFR-TKI Resistance in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Application to Biological Diagnostic and Monitoring
- PMID: 34638411
- PMCID: PMC8507869
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13194926
Molecular Mechanism of EGFR-TKI Resistance in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Application to Biological Diagnostic and Monitoring
Abstract
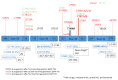
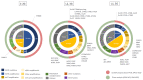
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common cancer in the world. Activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene mutations are a positive predictive factor for EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). For common EGFR mutations (Del19, L858R), the standard first-line treatment is actually third-generation TKI, osimertinib. In the case of first-line treatment by first (erlotinib, gefitinib)- or second-generation (afatinib) TKIs, osimertinib is approved in second-line treatment for patients with T790M EGFR mutation. Despite the excellent disease control results with EGFR TKIs, acquired resistance inevitably occurs and remains a biological challenge. This leads to the discovery of novel biomarkers and possible drug targets, which vary among the generation/line of EGFR TKIs. Besides EGFR second/third mutations, alternative mechanisms could be involved, such as gene amplification or gene fusion, which could be detected by different molecular techniques on different types of biological samples. Histological transformation is another mechanism of resistance with some biological predictive factors that needs tumor biopsy. The place of liquid biopsy also depends on the generation/line of EGFR TKIs and should be a good candidate for molecular monitoring. This article is based on the literature and proposes actual and future directions in clinical and translational research.
Keywords: EGFR mutations; cell-free DNA; molecular analysis; next-generation sequencing; non-small cell lung cancer; resistance mechanisms; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
D.R.: ArcherRx; L.P.: none; E.P.: none; E.G.: none; L.D.: none; V.R.: none; A.-C.V.: none; L.V.: none; C.M.: none; M.B.-F.: Astra-Zeneca, Pfizer, Amgen.
Figures


References
-
- Barlesi F., Mazieres J., Merlio J.P., Debieuvre D., Mosser J., Lena H., Ouafik L., Besse B., Rouquette I., Westeel V., et al. Biomarkers France contributors. Routine molecular profiling of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a 1-year nationwide programme of the French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT) Lancet. 2016;387:1415–1426. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00004-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leduc C., Merlio J., Besse B., Blons H., Debieuvre D., Bringuier P., Monnet I., Rouquette I., Fraboulet-Moreau S., Lemoine A., et al. French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT). Clinical and molecular characteristics of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR mutation: Results of the nationwide French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT) program. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28:2715–2724. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx404. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Russo A., Franchina T., Ricciardi G., Battaglia A., Picciotto M., Adamo V. Heterogeneous Responses to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) in Patients with Uncommon EGFR Mutations: New Insights and Future Perspectives in this Complex Clinical Scenario. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:1431. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061431. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

